When to Get a Hair Transplantation?
Hair loss is an issue that plagues millions of individuals across the globe, igniting feelings of insecurity and distress. Fortunately, advancements in medical technology have birthed effective solutions such as the hair transplant procedure. However, determining when it is the right time for such a transformative journey is essential. This comprehensive guide delves into various facets of hair loss, evaluates the factors influencing the decision for a hair transplantation, and examines both the potential benefits and risks involved. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision about whether a hair transplant aligns with your personal needs.
1. Understanding Hair Loss and Its Causes
In order to consider hair transplants and their implications, one must first comprehend the underlying causes of hair loss. Hair loss isn’t merely a cosmetic issue; it can stem from various medical conditions, genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors.
1.1. Androgenetic Alopecia: Male and Female Pattern Baldness
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly referred to as male or female pattern baldness, stands out as the most prevalent form of hair loss. It manifests typically through a receding hairline in men while women might experience thinning on the crown of the head. The root cause of this condition lies in genetics and hormonal influences, particularly a heightened sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone.
The emotional toll of androgenetic alopecia can be profound. Individuals may grapple with diminished self-worth and anxiety regarding their appearance. In many cases, the awareness of family history of hair loss could spur early intervention strategies, including hair transplants, before the situation escalates.
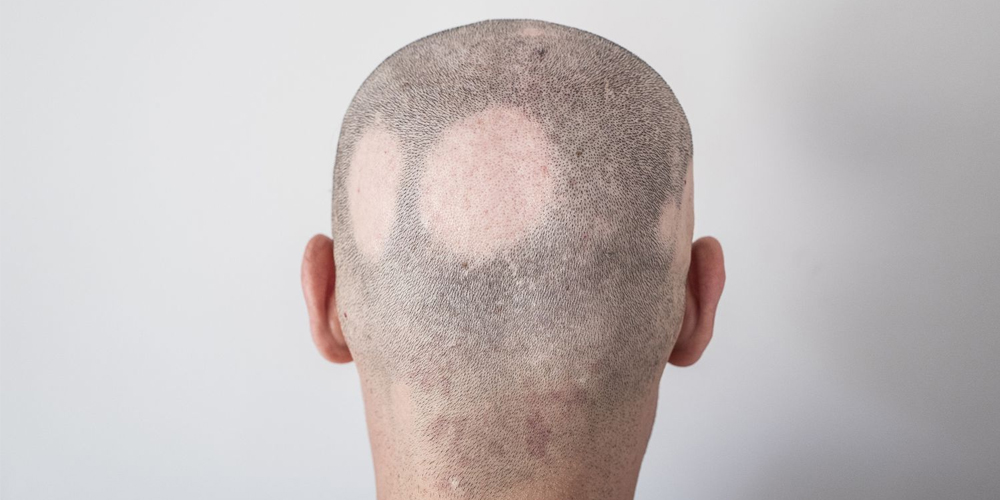
1.2. Alopecia Areata: An Autoimmune Challenge
Alopecia areata presents a contrasting picture to androgenetic alopecia. This autoimmune disorder results in patchy hair loss, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. The unpredictable nature of this condition can create significant emotional strain for those affected. Unlike androgenetic alopecia, the prospective treatment options, including hair transplants, require careful consideration.
Transplants for individuals with alopecia areata are generally discouraged unless the condition is well-controlled. This precaution stems from the risk of recurrence post-transplantation, which can lead to further frustration and disappointment.
1.3. Telogen Effluvium: Temporary Loss
Telogen effluvium represents another distinct type of hair loss characterized by temporary shedding. Typically triggered by stress, hormonal fluctuations, nutritional deficiencies, or certain medications, this condition can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. The good news is that telogen effluvium usually resolves itself once the underlying triggers are addressed.
Given its temporary nature, opting for a hair transplant may not be advisable for those suffering from telogen effluvium. Instead, focusing efforts on restoring overall health and managing stress levels could lead to natural regrowth.
1.4. Traction Alopecia: Tension and Styles
Traction alopecia arises due to continuous tension placed on the hair, often from tight hairstyles such as braids or weaves. The key to reversing this type of hair loss lies in alleviating the source of tension. In cases where permanent damage has occurred, hair transplants can serve as a viable option if scarring permits.
Maintaining healthy hair practices is essential to prevent traction alopecia. Educating oneself about safe hairstyles can foster long-term hair health.
1.5. Scarring Alopecia: Permanent Effects
Lastly, scarring alopecia entails the irreversible destruction of hair follicles due to inflammation caused by conditions such as lupus or folliculitis decalvans. Unfortunately, hair transplants are generally deemed unsuitable for individuals experiencing scarring alopecia because the damaged hair follicles cannot regenerate.
For those grappling with this diagnosis, alternative treatments like scalp micropigmentation might yield more favorable outcomes.
2. Deciding if a Hair Transplant is Right for You
Hair transplants can offer rejuvenating results for many individuals. Nevertheless, several critical considerations must be pondered before settling on this solution.
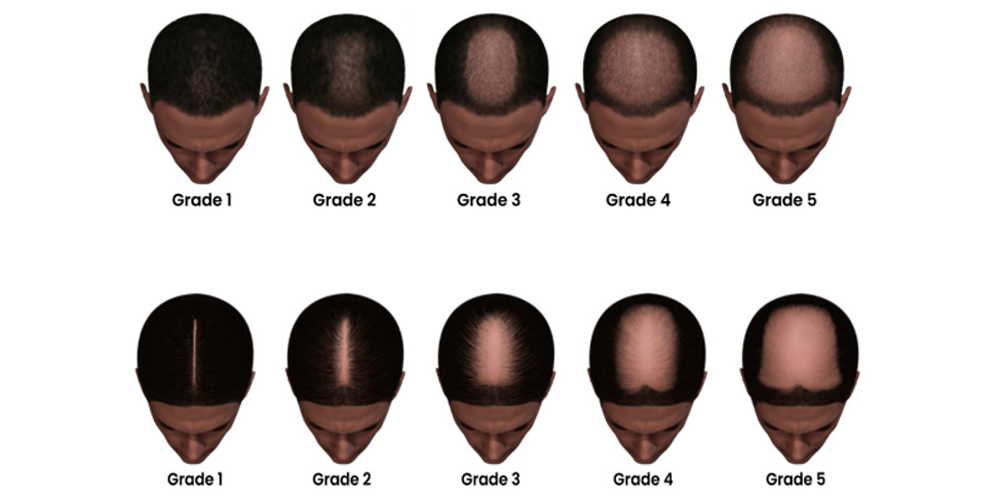
2.1. Type and Severity of Hair Loss
The type and severity of hair loss play pivotal roles in determining the appropriateness of a hair transplant.
In cases of androgenetic alopecia, early intervention can lead to excellent outcomes. If hair loss is limited to a receding hairline or minor thinning, individuals might find substantial success in achieving a fuller look through transplantation. Those in advanced stages, however, may face challenges such as insufficient donor hair supply, necessitating more extensive treatment or alternative methods.
Individuals struggling with alopecia areata should approach hair transplants cautiously. The autoimmune nature of the condition raises the possibility of post-transplant hair loss recurrence. Therefore, assessing the stability of the condition beforehand becomes vital.
On the other hand, telogen effluvium and traction alopecia, being primarily reversible conditions, often do not warrant surgical intervention. These situations require patience and support rather than drastic measures.

2.2. Availability of Donor Hair
The availability of donor hair can significantly influence the feasibility of a hair transplant. The donor area, typically located at the back and sides of the scalp, must possess enough healthy hair to ensure a successful procedure.
If the donor hair is abundant, candidates can expect positive outcomes. Conversely, limited donor hair may necessitate exploring alternative treatments such as scalp micropigmentation or hair systems.
2.3. Personal Expectations
Having realistic expectations surrounding hair restoration is crucial for individuals considering hair transplants. While these procedures can restore a fuller head of hair, they do not guarantee a miracle solution. Factors such as individual variations in healing and hair growth should be acknowledged.
Those undergoing hair transplants must also prepare for post-surgery care, which requires diligence, follow-up appointments, and patience as they wait for results to unfold. Understanding the reality of the process can alleviate disappointment later on.
2.4. Lifestyle and Habits
Lifestyle choices can substantially influence the success of a hair transplant. Smoking, for instance, poses several risks, including poor healing and increased complications post-surgery.
Excessive alcohol consumption also jeopardizes overall health and wound healing, adversely impacting transplant outcomes. Moreover, some medications can interfere with hair growth and recovery. Thus, individuals must inform their surgeons about any medications they take prior to surgery.
2.5. Age and Overall Health
While age alone does not disqualify anyone from receiving a hair transplant, maintaining good overall health is crucial for achieving satisfactory results. Underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or thyroid disorders, can hinder recovery processes.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle-characterized by balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and sufficient sleep-serves to optimize healing and enhance overall well-being.
3. The Hair Transplant Process Explained
Once the decision has been made to pursue a hair transplant, it’s vital to familiarize yourself with the process and what to expect.
3.1. Consultation and Assessment
The journey begins with a thorough consultation and assessment by a qualified surgeon. At this stage, your surgeon will evaluate your hair loss, discuss medical history, and explore lifestyle factors.
This interactive dialogue is paramount, as it establishes the foundation for a customized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs. Additionally, the surgeon will gauge donor hair supply and determine the most appropriate method for harvesting follicles.

3.2. Harvesting the Donor Hair
Donor hair can be harvested using two primary techniques: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS).
FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles one at a time using a small punch tool. This minimally invasive approach often results in less discomfort and quicker recovery.
FUSS, on the other hand, entails the removal of a strip of skin containing hair follicles from the donor area, which is then dissected into individual grafts. Although this method may leave a linear scar, it often allows for a greater number of grafts to be obtained in a single session.
3.3. Creating the Recipient Area
With donor hair harvested, the next step is preparing the recipient area. The surgeon meticulously creates tiny incisions or slits in the scalp where the hair grafts will be implanted.
This precision is vital to ensuring natural-looking results and comfortable healing. The skill of the surgeon during this phase directly impacts the aesthetic outcome of the procedure.
3.4. Graft Implantation
Following the preparation of the recipient area, the harvested hair grafts are carefully placed into the designated sites. Surgeons must pay attention to the angle and direction in which the grafts are inserted, emulating natural hair growth patterns.
This labor-intensive step requires concentration and expertise to achieve the desired outcome of a full and natural-looking head of hair.
3.5. Post-Surgery Care
After the procedure, the surgeon will provide detailed instructions to aid in optimal recovery. This includes guidelines for wound cleaning, medication use, and restrictions on physical activity.
Adhering to post-surgery care recommendations is crucial for minimizing complications and ensuring the longevity of results.
4. Benefits of a Hair Transplant
For many individuals, hair transplants bring about numerous advantages that extend beyond aesthetics.
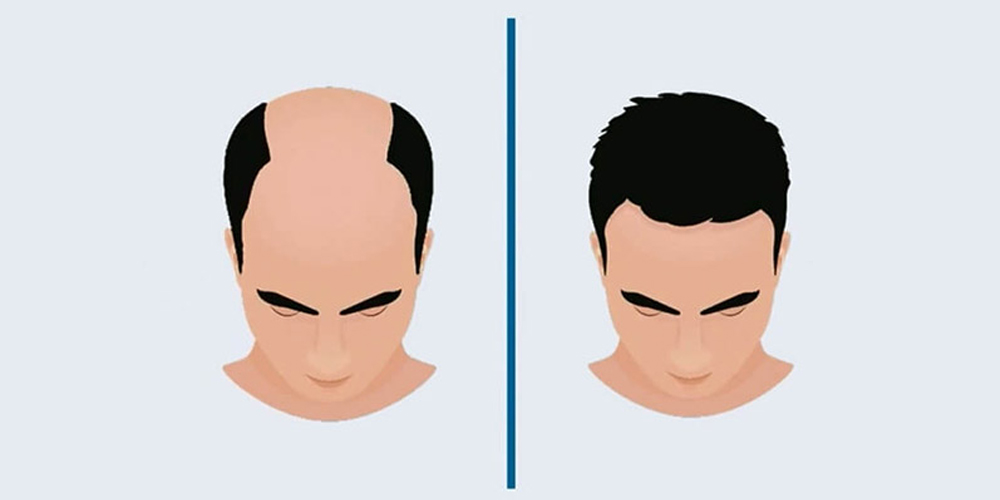
4.1. Natural-Looking Results
One of the most appealing aspects of hair transplants lies in their ability to yield natural-looking results. Transplanted hair integrates seamlessly with existing hair, and patients can enjoy renewed confidence as they showcase their revitalized appearance.
4.2. Permanent Solution
Unlike temporary fixes, transplanted hair follicles are considered permanent. Once successfully integrated, they continue to grow throughout a person's life, granting individuals the satisfaction of enduring results.
4.3. Increased Confidence and Self-Esteem
The psychological benefits of hair restoration are profound. For many, a full head of hair symbolizes youth and vitality, bolstering self-esteem and confidence.
Restoring one’s appearance can have a ripple effect-improving social interactions, career opportunities, and overall quality of life.
4.4. High Success Rates
When performed by skilled and experienced surgeons, hair transplants boast consistently high success rates. Many individuals who commit to the procedure are thrilled with the outcome, often reporting satisfaction with their new look.

5. Potential Risks and Complications of a Hair Transplant
Despite their myriad benefits, hair transplants come with inherent risks and potential complications.
5.1. Bleeding
Minor bleeding is a common occurrence following hair transplant surgery. While typically manageable, excessive bleeding could necessitate medical intervention.
Understanding this risk can encourage individuals to seek care promptly if they notice unusual symptoms during recovery.
5.2. Infection
Though infections are rare, they remain a potential concern if proper hygiene protocols and post-operative instructions are neglected.
Patients must remain vigilant in their aftercare routines, safeguarding against infections to ensure optimal healing.
5.3. Scarring
Scarring may develop in the donor area, regardless of the harvesting method utilized. While surgeons strive to minimize visible scars, some scarring is inevitable.
For individuals concerned about visible scars, discussing options with the surgeon beforehand can help set realistic expectations.
5.4. Hair Graft Rejection
In certain cases, the body’s immune system may reject transplanted hair follicles, resulting in hair loss. This possibility reinforces the importance of selecting an experienced surgeon, as technique plays a crucial role in minimizing rejection rates.
5.5. Uneven Growth
Post-transplant, some individuals may observe uneven hair growth. This inconsistency can arise due to various factors, including individual biology and adherence to aftercare guidelines.
In instances where results fall short of expectations, additional procedures may be required to correct uneven growth.
5.6. Unsatisfactory Aesthetics
Ultimately, the outcome of a hair transplant can vary from person to person. Factors such as unrealistic expectations, an inexperienced surgeon, and individualized biological responses can all contribute to unsatisfactory results.
Thus, conducting thorough research to select a qualified surgeon is paramount in achieving desired aesthetic goals.
Conclusion
Deciding when to get a hair transplant is undoubtedly a personal choice, shaped by a multitude of factors unique to each individual. Understanding the nuances of hair loss types, evaluating donor hair availability, setting realistic expectations, and considering financial implications are all essential steps in making an informed decision.
Whether you choose to embark on the path of hair restoration through a hair transplant or explore alternative treatments, remember that self-acceptance and mental well-being should always remain at the forefront of your journey. Ultimately, hair restoration can lead to renewed confidence and satisfaction, helping you embrace the vibrant individual you are meant to be.
LATEST POSTS








