Alopecia Areata: Can Patchy Hair Loss Be Treated?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that can leave sufferers feeling disheartened as they witness patches of hair loss on their scalp, eyebrows, or even their entire body. The unpredictable nature of this condition-where hair may grow back only to fall out again-can be emotionally taxing and lead to feelings of self-consciousness. While research into the precise causes remains ongoing, new treatments are emerging that provide hope for those affected by alopecia areata. This article will explore the various dimensions of alopecia areata, including its underlying mechanisms, symptoms, diagnosis, and the evolving landscape of treatment options.
1. Understanding Alopecia Areata: A Closer Look
1.1. What is Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata is defined by its sudden onset and distinctive presentation characterized by smooth, round patches of hair loss. Unlike other forms of hair loss that may occur due to aging, hormonal changes, or medication, alopecia areata is rooted in an autoimmune response. Here, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss in localized areas.
The emotional impact of this condition cannot be overstated. Individuals often grapple with feelings of shame, frustration, and isolation as they navigate the social implications of visible hair loss. For many, alopecia areata becomes not just a physical problem but an emotional journey that can affect various aspects of daily life, including social interactions, self-esteem, and overall mental health.
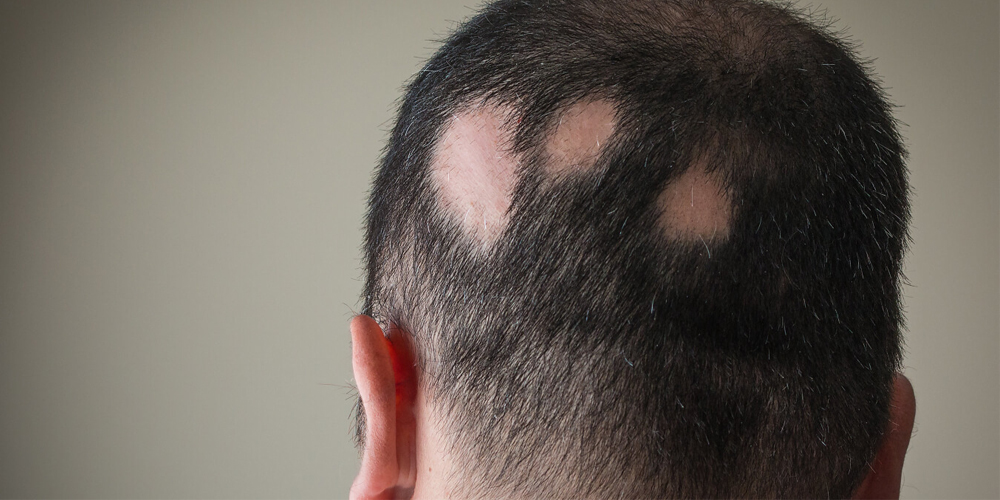
1.2. The Trigger: Genetics and Environment
While the exact triggers for alopecia areata remain elusive, current research points toward a complex interplay between genetic predispositions and environmental factors:
Genetics: Individuals with a family history of alopecia areata are at a higher risk for developing the condition themselves, indicating a significant genetic component. Various genes associated with immune system regulation and hair follicle biology have been implicated, though no single gene has been conclusively identified as responsible.
Environmental Factors: Beyond genetics, environmental stressors play a crucial role. Psychological stress, infections, and certain medication use can exacerbate or even trigger episodes of hair loss. The relationship between these environmental factors and the immune system's dysfunctional behavior is an area of active study and may one day yield insights into preventive strategies.
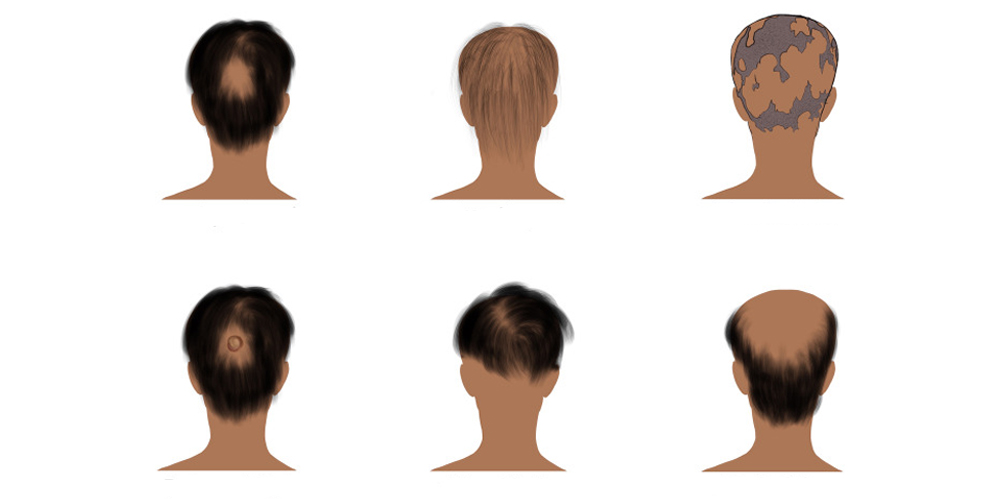
1.3. The Spectrum of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata exists on a spectrum, with different forms exhibiting varying degrees of hair loss:
Common Forms
- Alopecia Areata: Characterized by small, isolated patches of hair loss on the scalp, this form is the most prevalent.
- Alopecia Totalis: When individuals experience complete hair loss on the scalp, it can dramatically alter one's appearance and sense of identity.
- Alopecia Universalis: This severe form involves total hair loss across the entire body, posing unique challenges for those affected.
Other Variants
Additional forms like ophiasis, which presents as a band-like hair loss around the scalp, and alopecia areata inversa, affecting areas such as the beard and underarms, show the diverse presentations of this condition. Each form poses different psychological and social ramifications for the individual and may require specialized treatment approaches.
2. Diagnosing Alopecia Areata: A Multi-Pronged Approach
2.1. Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing alopecia areata typically begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. Physicians will inquire about family history, recent life stressors, and any medications being taken. Observation of the hair loss pattern, along with other signs of autoimmune diseases, guides the clinical assessment.
Additional Diagnostic Tools
In specific cases, doctors may resort to diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- Microscopy: Examining a sample of hair under a microscope can reveal characteristic signs of alopecia areata, assisting in confirming the diagnosis.
- Biopsy: A skin biopsy may be performed to analyze the structure of hair follicles and rule out other dermatological conditions.
- Blood Tests: These can identify markers for other autoimmune disorders or deficiencies contributing to hair loss.
2.2. Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis helps tailor treatment options effectively. Distinguishing alopecia areata from other causes of hair loss ensures that patients receive appropriate interventions. Furthermore, identifying coexisting autoimmune disorders can significantly influence treatment strategies and patient management.
3. Treatment Options: A Spectrum of Hope
3.1. Topical Therapies
Topical therapies are among the first lines of treatment for alopecia areata, aiming to stimulate hair regrowth while reducing inflammation.
Minoxidil: Originally developed to treat high blood pressure, minoxidil is now widely used in both men and women to address hair loss. Its effectiveness in alopecia areata varies, but some users report positive results. Minoxidil works by improving blood circulation in the scalp and stimulating hair follicles to promote new hair growth.
Anthralin: Anthralin is a coal tar derivative that aids in managing skin cell growth and inflammation, potentially fostering hair regrowth. Though effective, it requires consistent application and can cause irritation, necessitating close follow-up with a healthcare provider.
3.2. Systemic Therapies
When topical treatments fail or when the condition is more extensive, systemic therapies may be recommended.
Immunosuppressants: Medications like methotrexate and cyclosporine can suppress the immune system's activity, promoting hair growth. While promising, these drugs carry risks of adverse reactions and are usually reserved for severe cases of alopecia areata.
Biological Therapies: Emerging biologics, particularly Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors such as tofacitinib and ruxolitinib, represent a new class of treatment targeting the immune response associated with alopecia areata. Clinical trials are underway to ascertain their long-term safety and efficacy, showcasing a potential breakthrough in therapeutic strategies.
3.3. Light Therapy
Light therapy utilizes ultraviolet (UV) light to promote hair regrowth in some individuals. Though the precise mechanism of action remains unclear, UV light exposure may help modulate immune responses and invigorate hair follicles. This method may be combined with other treatments to enhance overall effectiveness.
3.4. Complementary Therapies
While they may not directly treat alopecia areata, complementary therapies can alleviate emotional distress and improve overall well-being.
Stress Management Techniques
Since stress can trigger or aggravate alopecia areata, engaging in stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises may prove beneficial. These practices promote relaxation and adaptability, aiding in coping with both the physical and emotional challenges associated with hair loss.
3.5. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, ensuring adequate sleep, and maintaining a regular exercise routine can positively affect overall health. While lifestyle changes may not directly reverse hair loss, they can contribute to improved mental health and foster resilience during the journey of living with alopecia areata.

3.6. Hair Restoration Options
For those seeking immediate solutions to manage the aesthetic aspects of hair loss, several hair restoration options can enhance confidence and self-image.
Hairpieces or Wigs: Hairpieces and wigs offer a versatile and natural-looking alternative for individuals who wish to conceal hair loss. Modern advancements have led to high-quality options that blend seamlessly with natural hair, allowing wearers to feel more comfortable and confident.
Scalp Micropigmentation: This cosmetic technique involves applying tiny pigment dots to the scalp to give the appearance of fuller hair. It mimics the look of hair follicles, effectively disguising bald patches and offering an instant boost in self-esteem.
Hair Transplantation: Surgical hair transplantation entails relocating hair follicles from healthy areas to balding spots. While this approach offers a permanent solution, it comes with costs and requires multiple sessions for optimal results.
4. Navigating Treatment: An Individualized Approach
Tailoring Treatments to Individual Needs: There is no universal treatment for alopecia areata; instead, the best outcomes often arise from personalized care plans. Individual preferences, severity of hair loss, and response to previous interventions must all be considered when devising a treatment strategy.
Patience and Persistence: Given alopecia areata's unpredictable nature, patience is key. Treatments may take time to yield visible results, and relapses can occur. Adopting a resilient mindset can facilitate coping through these challenging cycles.
Monitoring for Side Effects: All treatments carry potential side effects. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers to monitor for any adverse reactions ensure that adjustments can be made promptly to optimize treatment and maintain health.
5. Living with Alopecia Areata: Embracing Your Journey
Emotional Resilience: Living with alopecia areata can evoke a myriad of emotions, from frustration to acceptance. Recognizing the emotional toll of this condition is essential for developing coping strategies. Building emotional resilience through supportive networks, therapy, and self-care practices can empower individuals to embrace their journey.
Seeking Professional Help: Therapists specializing in body image issues or chronic illness can guide individuals through the emotional landscape of living with alopecia areata. Constructive coping mechanisms, emotional support, and tools for building self-esteem can significantly enhance resilience during challenging times.
Prioritizing Self-Care: Investing time in self-care activities that nurture the mind, body, and spirit can bolster emotional well-being. Activities such as spending time outdoors, pursuing hobbies, or practicing mindfulness contribute to overall happiness and serve as protective factors against the emotional impacts of hair loss.
Embracing Uniqueness: Ultimately, learning to embrace one's uniqueness is pivotal. Recognizing that alopecia areata is one facet of a person's identity-and not the entirety of it-allows individuals to reclaim their narrative. Celebrating personal strengths and accomplishments can shift the focus away from hair loss to holistic self-worth.
Conclusion
While a cure for alopecia areata remains an unfulfilled quest, substantial progress in research and treatment options brings hope for a brighter future. By understanding the intricacies of the condition and adopting personalized treatment approaches, individuals can navigate the journey of living with alopecia areata with greater resilience and empowerment. As the landscape of treatment evolves, so too does the possibility of reclaiming not only hair but also confidence and self-identity.
LATEST POSTS








