Hair Loss: Causes and Treatments
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, is a widespread concern that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be a natural part of the aging process, but it can also be a symptom of underlying health conditions. Understanding the potential causes of hair loss and the available treatments is crucial for finding effective solutions and restoring a full head of hair.
1. Hereditary Factors (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in both men and women. This condition is influenced by genetics and hormonal factors, leading to progressive thinning of the hair follicles.
1.1. Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Male pattern baldness is the most prevalent type of hair loss in men, affecting approximately 50% of men over the age of 50. It is characterized by a receding hairline and thinning hair on the crown of the head, eventually leading to partial or complete baldness.
The primary cause of male pattern baldness is genetics, specifically the influence of androgen hormones on hair follicles. Testosterone, the main androgen hormone in men, is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase. DHT then binds to receptors on hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner and shorter hairs until they eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Other contributing factors to male pattern baldness include age, stress, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. While there is no cure for this condition, several treatment options can help slow down its progression and promote hair regrowth.
1.2. Female Pattern Baldness
Female pattern baldness is the female equivalent of male pattern baldness, with similar characteristics and underlying causes. However, it progresses more gradually in women and rarely leads to complete baldness.
Like male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness is also influenced by genetics and hormonal factors, specifically the sensitivity of hair follicles to androgen hormones. It typically presents as thinning hair on the crown and a widening part, with the frontal hairline remaining intact.
As with male pattern baldness, there is no cure for female pattern baldness, but various treatments can help improve hair density and slow down its progression.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can have a significant impact on hair growth, causing temporary or permanent hair loss. The following are some situations where hormonal changes can lead to hair loss:
2.1. Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of significant hormonal changes in a woman's body, which can affect hair growth. During pregnancy, increased levels of estrogen prolong the growth phase of hair, resulting in thicker and fuller hair. However, after childbirth, estrogen levels drop drastically, leading to a shedding of this excess hair. This process is known as telogen effluvium and usually resolves within six months after giving birth.
2.2. Menopause
During menopause, a woman's estrogen levels decline, leading to imbalances in other hormones such as testosterone and DHT. These hormonal changes can result in hair thinning and hair loss, similar to male and female pattern baldness. While not all women will experience hair loss during menopause, it is a common occurrence for those who have a family history of female pattern baldness.
2.3. Thyroid Disorders
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism and hormone production. Therefore, an imbalance in thyroid hormones can affect various bodily functions, including hair growth. Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can result in hair loss, with hypothyroidism being the most common cause. Fortunately, treating the underlying thyroid condition can often reverse hair loss and promote regrowth.
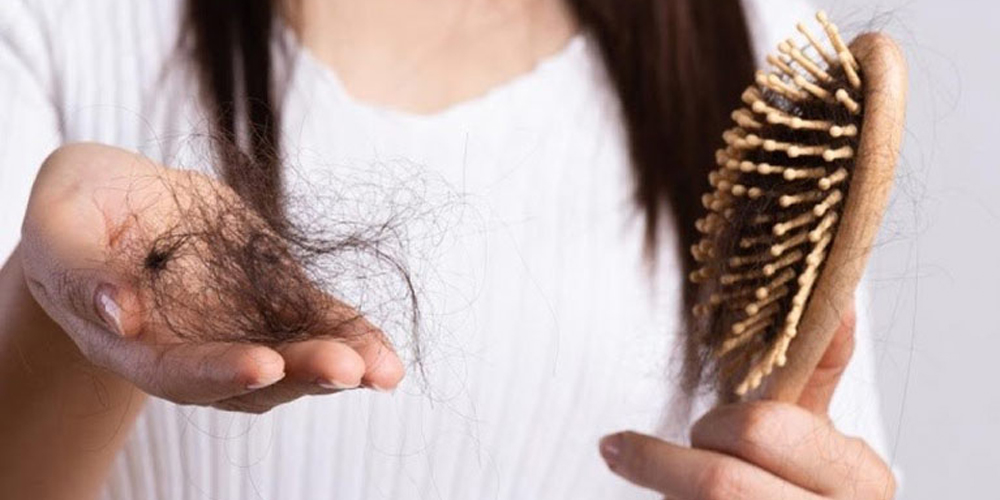

3. Medical Conditions and Medications
Several medical conditions and medications can also cause hair loss. Here are some of the most common ones:
3.1. Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss on the scalp and other areas of the body. The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to inflammation and hair loss. While the exact cause of this condition is unknown, it is believed to be triggered by stress, genetics, or environmental factors.
Treatment for alopecia areata varies depending on the severity of hair loss and may include topical steroids, oral medications, or injections of corticosteroids directly into the affected areas.
3.2. Scalp Infections
Infections of the scalp, such as ringworm, can cause scaly patches and hair loss. These infections are usually treated with antifungal medications, which can help stop hair loss and promote regrowth.
3.3. Lupus
Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause widespread inflammation and damage to various organs, including the skin. Hair loss is a common symptom of lupus, known as discoid lupus. It presents as round lesions on the scalp that can scar and lead to permanent hair loss. Treatment for lupus-related hair loss involves controlling the underlying condition and using medications to minimize inflammation.
3.4. Certain Medications
There are several prescription medications whose side effects include hair loss. Chemotherapy drugs are well-known for causing hair loss, but other medications like blood thinners, beta blockers, and antidepressants can also lead to hair loss. In most cases, hair growth will resume once you stop taking these medications, but it may take several months.
4. Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Stress and lifestyle choices can also play a role in hair loss. Here are some examples:
4.1. Telogen Effluvium
Chronic stress and trauma can lead to telogen effluvium, a type of hair loss characterized by excessive shedding all over the scalp. This condition can occur due to physical or emotional stressors, such as illness, surgery, drastic weight loss, or emotional trauma. Telogen effluvium is usually temporary, and hair growth will resume within six months after the underlying stressor is removed.
4.2. Nutritional Deficiencies
The hair follicles require specific nutrients to grow and maintain healthy hair. A diet lacking in essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, can lead to hair thinning and hair loss. In most cases, addressing these deficiencies through dietary changes or supplements can help promote hair regrowth.
4.3. Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to hair loss, primarily by reducing blood flow to the scalp and damaging the hair follicles. Additionally, smoking has been linked to increased levels of DHT, the hormone responsible for male and female pattern baldness. Therefore, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can have a positive impact on hair health.

5. Available Treatments for Hair Loss
The treatment options for hair loss vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some of the most common treatments:
5.1. Medications
Medications are often prescribed for hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, and other factors that affect hair growth. Some of the most commonly used medications include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This topical medication is available over-the-counter and is effective in promoting hair growth in both men and women with androgenetic alopecia.
- Finasteride (Propecia): This prescription medication is only approved for use in men and works by blocking the conversion of testosterone into DHT, thereby preventing further hair loss.
- Spironolactone: This medication is commonly prescribed for women with hair loss due to hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Corticosteroids: These medications can be prescribed in various forms, including topical creams, injections, or pills, to treat different types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata and discoid lupus.
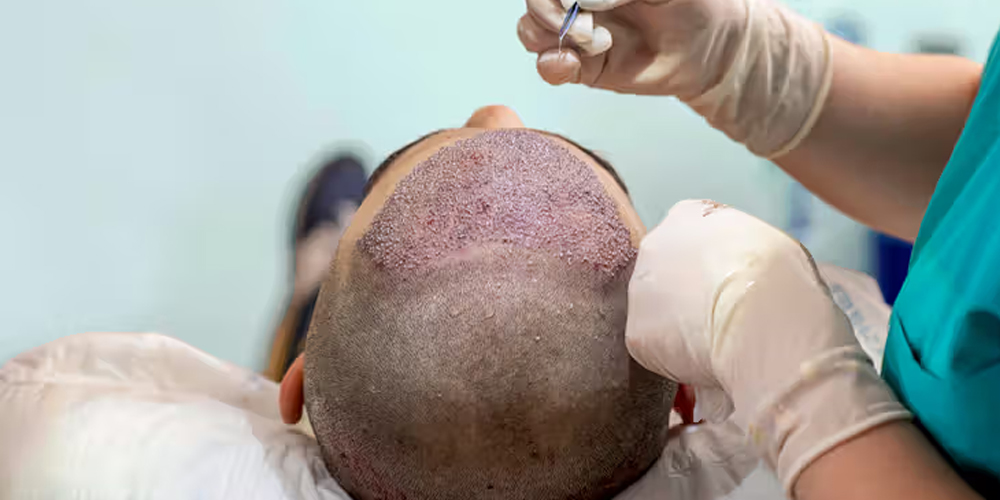
5.2. Hair Transplant Surgery
In cases of significant hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This procedure involves taking hair follicles from one area of the scalp (usually the back of the head) and transplanting them to areas where there is thinning or no hair. The transplanted hair will continue to grow and typically provides a permanent solution to hair loss.
5.3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment that involves exposing the scalp to low levels of red light to stimulate hair growth. LLLT is believed to work by increasing blood flow to the scalp and promoting cellular metabolism in hair follicles. While research on its effectiveness is ongoing, some studies have shown promising results in improving hair density and thickness.
5.4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient's own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. Platelets contain growth factors that can promote cell growth and repair damaged tissues. PRP therapy is typically used to treat hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia and has shown promising results in promoting hair regrowth.
6. Lifestyle Changes for Healthy Hair
In addition to medical treatments, making some lifestyle changes can also help improve the health and appearance of your hair. Here are some tips to incorporate into your daily routine:
- Maintain a healthy and well-balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Avoid hairstyles that put excessive tension on your hair, such as tight ponytails or braids.
- Use gentle hair care products and avoid over-styling or using heat on your hair.
- Protect your hair from sun damage by wearing a hat or using protective products with SPF.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or seeking professional help if needed.
Conclusion
Hair loss is a common concern that can have various underlying causes. While some forms of hair loss are permanent, others can be treated effectively with the right approach. It is essential to understand the potential causes and available treatments for hair loss to find the best solution for your specific condition. If you are experiencing excessive hair loss, consult with a medical professional to determine the underlying cause and develop a personalized treatment plan to restore your full head of hair. Remember, healthy hair starts with a healthy lifestyle, so make sure to take care of your overall well-being for optimal hair health.
LATEST POSTS








