When To Talk To your Doctor About Hair Loss
Hair loss is a concern that resonates with millions of individuals across the globe, transcending age, gender, and ethnicity. It can manifest as a minor inconvenience for some or evolve into a distressing symptom of underlying health issues for others. While shedding hair is part of our natural cycle-losing roughly 50 to 100 hairs daily-it’s crucial to recognize when this phenomenon escalates beyond normalcy. Understanding the nuances of hair loss and identifying its triggers can empower individuals to seek timely medical intervention, ultimately preserving both their hair and overall well-being.
1. Understanding the Basics of Hair Loss
Before navigating through the intricate details of hair loss, it’s pertinent to start with some foundational knowledge. Our hair undergoes a continuous growth cycle-growth, resting, and shedding-regulated by various factors. This cyclical nature inherently allows for occasional hair loss; however, interruptions in this process can lead to excessive shedding or thinning, signaling possible health concerns.
The hair growth cycle primarily consists of three phases: anagen (growth), telogen (resting), and catagen (transition). During the anagen phase, hair actively grows, lasting several years. Following this is the telogen phase, wherein hair remains dormant before eventually shedding. On average, people might shed between 50 to 100 strands daily without cause for alarm. However, if you begin to notice significantly more hair loss than usual, or your hair appears thinner than before, it is time to assess the situation further.
Understanding how different elements-such as genetics, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions-affect this cycle can help determine whether your experiences fall within the realm of normalcy or signal a burgeoning issue requiring professional evaluation.
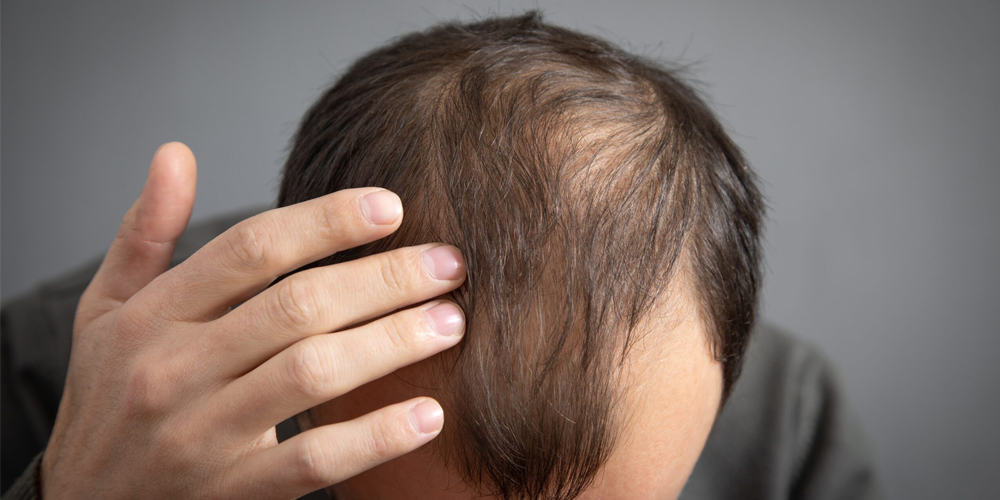

1.1. The Role of Genetics in Hair Loss
Genetics plays a fundamental role in determining the likelihood and pattern of hair loss one may experience throughout their life.
Androgenetic Alopecia, commonly referred to as male or female pattern baldness, is the most prevalent form of hair loss linked to genetic predisposition. In men, this condition typically results in a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while women often notice diffuse thinning along the scalp. This hereditary tendency can be inherited from either side of the family and often manifests as early as the late teenage years or early twenties.
Understanding your family history concerning hair loss can provide insight into what to expect as you age. Recognizing the signs earlier empowers individuals to take preemptive action, such as consulting a dermatologist or exploring early treatment options.
1.2. Hormonal Changes and Their Impact on Hair Health
Hormonal fluctuations can have significant impacts on hair health, leading to conditions such as Telogen Effluvium. This phenomenon can arise from various situations, including stress, pregnancy, illness, or hormonal changes during menopause or adolescence.
When hormonal levels shift suddenly, a significant portion of hair follicles may prematurely enter the telogen phase, resulting in pronounced shedding. Unlike androgenetic alopecia, which is progressive, telogen effluvium is often temporary and reversible once the underlying trigger is addressed.
It’s important to differentiate between the two types of hair loss, as both require different approaches for management or treatment.
1.3. Nutritional Deficiencies and Overall Hair Wellness
Another critical aspect of hair loss revolves around nutrition. The body requires specific vitamins, minerals, and proteins to sustain healthy hair growth. Deficiencies in essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, biotin, and protein can profoundly impact hair health, leading to increased shedding and slowed growth.
Engaging in a balanced diet that fulfills these nutrient needs is vital for maintaining strong, vibrant hair. If you suspect you are experiencing hair loss due to inadequate nutrition, consult with a healthcare provider who can recommend appropriate dietary adjustments or supplements.
2. Common Causes of Hair Loss
Numerous factors contribute to hair loss, each varying in severity and implications. An understanding of these causes can assist in determining when the situation might necessitate professional intervention.
2.1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness)
As previously mentioned, androgenetic alopecia is genetically driven and represents the most common cause of hair loss in both men and women.
In men, the condition typically begins with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown. Over time, these areas may merge, leading to extensive balding. For many men, acceptance of this reality can be a lengthy process; however, embracing available treatments or hair restoration methods can help maintain some degree of confidence as they manage the condition.
In women, the manifestation of androgenetic alopecia is often less pronounced but no less impactful. Women tend to experience diffuse thinning across the scalp rather than distinct bald spots. This presents unique psychological challenges, as societal expectations often tie femininity to full, healthy hair. Many women may find solace in treatments designed to stimulate hair growth or cosmetic solutions to improve appearance.
Recognizing the signs of androgenetic alopecia is pivotal for early intervention, which may slow progression and foster a supportive environment for affected individuals.
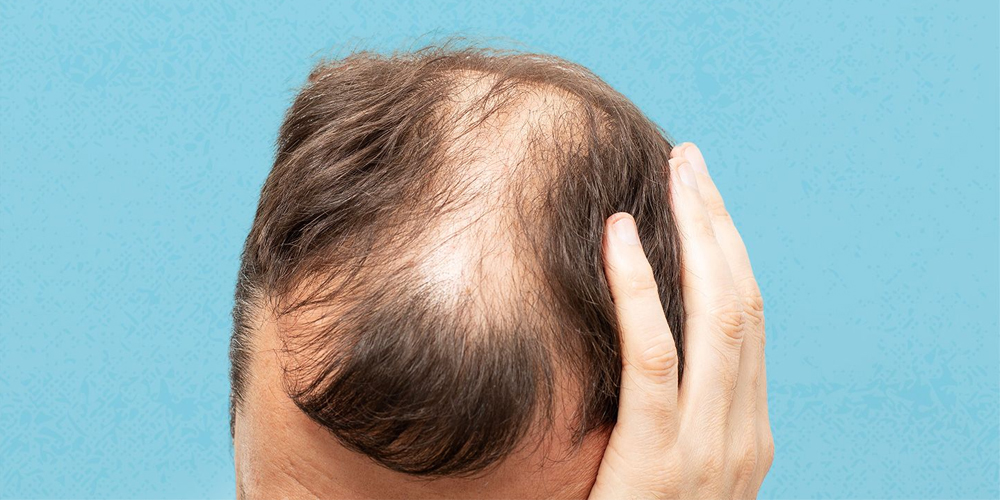
2.2. Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium presents a temporary yet alarming experience for those affected. Whether triggered by stress, significant physical trauma, or hormonal changes, the sudden onset of shedding can leave individuals feeling helpless.
Stress-induced telogen effluvium is particularly noteworthy. Prolonged emotional distress can result in considerable hair loss even months after the stressful event has subsided. It serves as a reminder of the profound connection between mental health and physical wellbeing. Individuals facing this condition must prioritize self-care and stress management strategies to facilitate recovery, demonstrating the importance of holistic approaches to health.
Postpartum hair loss, another variant of telogen effluvium, embodies the impact of hormones on hair health. After childbirth, many women notice increased shedding due to significant hormonal shifts. Understanding this phenomenon can provide peace of mind, reassuring new mothers that their experiences are typical and often transient.
2.3. Autoimmune Disorders
Alopecia Areata is another notable cause of hair loss that arises from autoimmune disorders. Individuals with this condition experience patchy hair loss as their immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to unpredictable bald spots.
Living with alopecia areata can be emotionally taxing. The unpredictable nature of the disease can result in feelings of anxiety or depression, amplifying the distress of seeing patches of hair missing. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans can help manage the condition effectively, fostering resilience among those impacted.
2.4. Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia)
While scarring alopecia is less common, it entails severe and irreversible hair loss caused by inflammation and destruction of hair follicles. The potential for permanent damage highlights the necessity for prompt medical intervention.
Various factors can contribute to scarring alopecia, including infections, autoimmune diseases, or burns. Individuals experiencing unusual itching, burning sensations, redness, or discomfort on the scalp should seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis is vital in preventing further damage, emphasizing the need for vigilance in monitoring any unusual scalp conditions.
3. When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding when hair loss demands immediate attention is essential for timely intervention. Not all hair loss requires medical consultation, but certain signs and symptoms can indicate a more serious underlying issue.
3.1. Sudden and Excessive Hair Loss
Experiencing a sudden increase in hair loss can be alarming, especially when accompanied by thinning or bald patches.
This abrupt change warrants immediate consultation with a healthcare professional. Conditions like telogen effluvium or alopecia areata require appropriate diagnosis and management to prevent further complications. Engaging in open conversations with medical professionals about concerns can alleviate anxiety surrounding the issue.
3.2. Hair Loss in Patches
If you notice patchy hair loss appearing abruptly and without discernible cause, this could be a sign of alopecia areata.
Timely diagnosis is crucial in managing the autoimmune disorder effectively. Dermatologists recommend early treatment interventions, as they may lead to better outcomes. Psychological support may also be beneficial for individuals coping with the emotional ramifications of uneven hair loss.
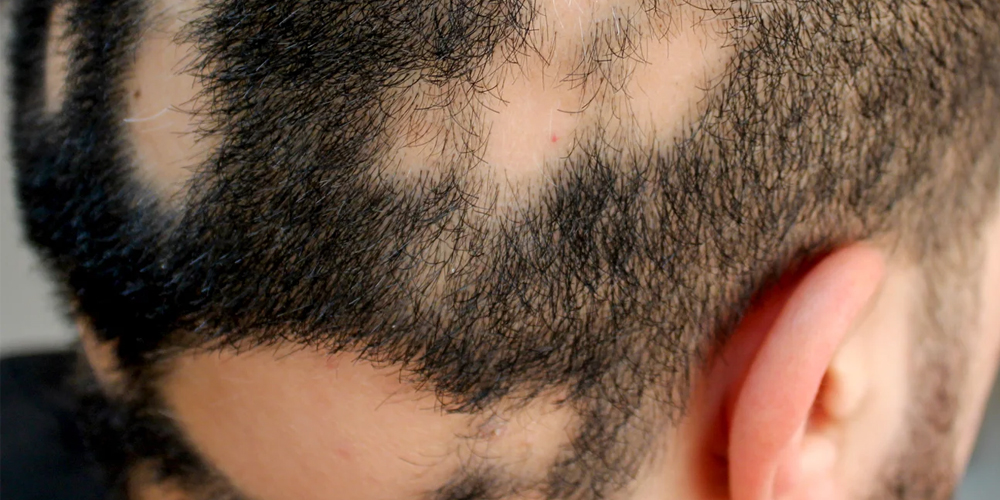
3.3. Unusual Hair Loss Patterns
An increase in hair loss following an atypical pattern-such as a rapidly receding hairline or localized thinning-should not be overlooked.
Keeping track of these changes and documenting patterns may aid dermatologists in diagnosing underlying conditions like androgenetic alopecia or other systemic health issues. This proactive approach fosters a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers, enhancing the accuracy and efficacy of treatment.
3.4. Related Symptoms
Hair loss isn’t always an isolated issue. If it occurs alongside other symptoms such as fatigue, unexplained weight loss, skin rashes, or nail changes, it’s imperative to seek medical advice promptly.
These symptoms might suggest underlying medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases. A comprehensive assessment can help address multiple health concerns simultaneously, streamlining the diagnostic process.
3.5. Life Events Triggering Hair Loss
Life-altering events-such as surgery, severe illness, childbirth, or emotional trauma-can instigate telogen effluvium, leading to notable hair loss.
While this type of hair shedding is often temporary, understanding the physiological response to stressors can guide individuals toward effective coping mechanisms. Consulting a doctor can help rule out additional factors contributing to hair loss and provide reassurance that the situation may rectify itself over time.
3.6. Family History of Hair Loss
For those with a family history of premature hair loss, closely monitoring one’s hair health becomes essential.
Taking proactive steps by seeking medical advice at the first signs of hair thinning can facilitate early intervention. This foresight can prove invaluable in managing genetic predispositions effectively.
3.7. Persistent Hair Loss Despite Self-Care Efforts
If hair loss continues despite trying various home remedies or over-the-counter treatments, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
Persistent shedding may indicate underlying medical conditions that require targeted treatment efforts. Seeking professional guidance can streamline the process of identifying the root cause, empowering individuals with informed choices regarding their hair health.
4. Diagnostic Procedures for Hair Loss
When seeking medical advice for hair loss concerns, a thorough examination will likely ensue. Healthcare providers may carry out several diagnostic tests to unearth the underlying cause.
4.1. Scalp Biopsy
A scalp biopsy involves removing a small sample of the scalp for microscopic examination.
This process can reveal signs of inflammation, infection, or abnormalities in the hair follicles, providing valuable insights into the possible causes of hair loss. Patients can benefit from understanding the rationale behind this test, as it can guide future treatment options.
4.2. Blood Tests
Blood tests serve as a vital tool in assessing overall health and identifying underlying medical conditions.
Conditions such as thyroid disorders, iron deficiency anemia, or hormonal imbalances may contribute to hair loss. Understanding one’s blood chemistry enables healthcare professionals to tailor treatment strategies that address both hair loss and any concurrent health issues.
4.3. Pull Test
The pull test involves gently tugging on a section of hair to gauge how many strands shed during the process.
This simple evaluation helps determine the extent of hair loss and may guide physicians in assessing the hair growth cycle's stability. Clear communication regarding the purpose and outcomes of the pull test can enhance patient understanding and cooperation.
4.4. Microscopic Examination
Microscopic examinations scrutinize hair under magnification, offering insights into the hair growth cycle and revealing potential signs of disease or damage.
This detailed analysis enriches the diagnostic process, paving the way for evidence-based treatment recommendations. Patients can appreciate the benefits of these assessments, knowing that each step adds to the broader picture of their hair health.
4.5. Light Microscopy
Light microscopy serves as a specialized technique to identify fungal infections or inflammatory conditions affecting hair loss.
By employing targeted methodologies, healthcare providers can develop more precise treatment plans that address the specific causes of hair loss. Open discussions about these assessments encourage a sense of partnership between patients and medical professionals.
5. Treatment Options for Hair Loss
Once the underlying cause of hair loss is identified, various treatment options may be considered based on individual needs.
5.1. Topical Medications
Minoxidil (Rogaine) is one of the most widely recognized topical medications aimed at stimulating hair growth and slowing down hair loss.
Individuals using minoxidil often see positive results, though consistency and patience are key to achieving desired outcomes. Exploring various applications of topical treatments encourages individuals to engage actively in their hair health journey.
5.2. Oral Medications
Conversely, oral medications such as finasteride (Propecia) specifically target male pattern baldness.
However, caution is necessary, as finasteride can cause birth defects in women. Understanding the importance of tailored treatments ensures individuals utilize safe and effective options that align with their specific circumstances.
5.3. Hair Transplantation
For those seeking more definitive solutions, hair transplantation offers a surgical option involving the relocation of hair follicles from denser regions of the scalp to areas of thinning.
This procedure can create a fuller appearance and significantly boost self-esteem. Discussing the risks, benefits, and expectations of hair transplantation helps individuals make informed decisions about aesthetic improvements.
5.4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves extracting concentrated platelets from an individual’s blood and injecting them into the scalp to promote hair growth.
This innovative approach leverages the body’s healing properties, fostering a sense of empowerment in the treatment process. As with any medical intervention, being well-informed about PRP therapy allows individuals to set realistic expectations regarding potential outcomes.
5.5. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy utilizes devices emitting low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and enhance blood flow to the scalp.
As a non-invasive approach, LLLT presents an attractive alternative for individuals seeking less aggressive treatments. Embracing diverse therapeutic modalities emphasizes the importance of personalized care in addressing hair loss.
6. Lifestyle Changes for Hair Health
Beyond medical interventions, implementing lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to healthier hair and potentially mitigate hair loss.
6.1. Stress Management Techniques
Managing stress stands out as a vital component of maintaining optimal hair health.
Engaging in exercises like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness practices can combat stress-related hair loss and improve overall well-being. Prioritizing self-care establishes a foundation for resilience against the adverse effects of stress on the body, including hair health.
6.2. Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients-such as proteins, iron, zinc, and vitamins-supports hair growth and contributes to overall health.
Choosing whole foods over processed options empowers individuals to nourish their bodies effectively. Incorporating diverse food groups enhances both nutritional intake and the satisfaction derived from meals, fostering a positive relationship with food.
6.3. Gentle Hair Care Practices
Embracing gentle hair care practices-avoiding harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles-prevents damage and breakage.
Investing in quality hair products that cater to one’s specific hair type ensures proper nourishment and minimizes risk factors associated with hair loss. Adopting gentle practices creates an environment where hair can thrive without undue stress.
6.4. Scalp Massage
Regularly massaging the scalp can improve blood circulation and bolster hair follicle health.
This simple yet effective practice fosters relaxation and encourages hair growth through enhanced nutrient delivery. Demonstrating the connection between self-care and hair health underscores the significance of nurturing oneself holistically.
6.5. Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Steering clear of smoking and limiting alcohol intake can positively impact hair health and overall well-being.
The harmful substances in tobacco and the negative effects of excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with nutrient absorption and impair hair growth. Promoting healthier lifestyle choices cultivates a supportive environment for vibrant hair.
Conclusion
Hair loss can indeed be distressing, yet it’s essential to recognize that it often represents a treatable condition. While some shedding is a natural occurrence, experiencing sudden, excessive, or unusual hair loss necessitates seeking medical advice. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can greatly enhance the likelihood of successfully managing hair loss and preserving your hair.
Consulting a dermatologist or healthcare professional provides valuable insights into the underlying causes of your hair loss and facilitates the development of a personalized treatment plan that aligns with your needs and preferences. Remember, open communication with your doctor, coupled with lifestyle modifications and suitable medical treatments, can make a significant difference in addressing your hair loss concerns, allowing you to maintain the health and vibrancy of your crowning glory.
LATEST POSTS