What is a Hair Follicle: Structure and Function Overview
When we talk about hair, one of the most fundamental questions that arise is: What is a Hair Follicle? Understanding hair follicles is essential for grasping how hair grows, how it can be affected by various conditions, and what roles they play in our overall health. Hair follicles are not merely vessels for hair growth; they are intricate structures that contribute significantly to skin health, thermoregulation, and sensory perception. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of hair follicles, exploring their structure, function, and significance in our lives.
1. The Anatomy of a Hair Follicle
The anatomy of a hair follicle is crucial to understanding its purpose and functionality. Every hair follicle is a miniature organ that plays several roles, and its design reflects this complexity.
1.1. The Basic Structure
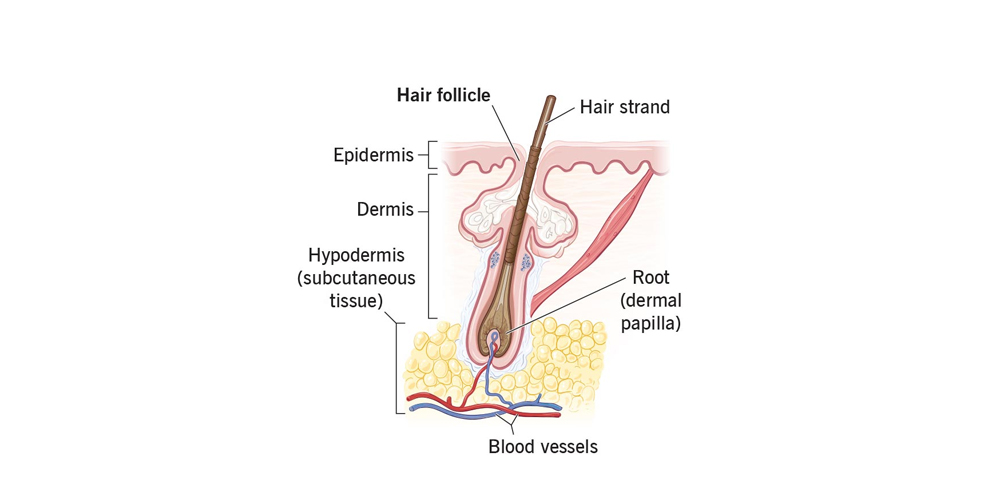
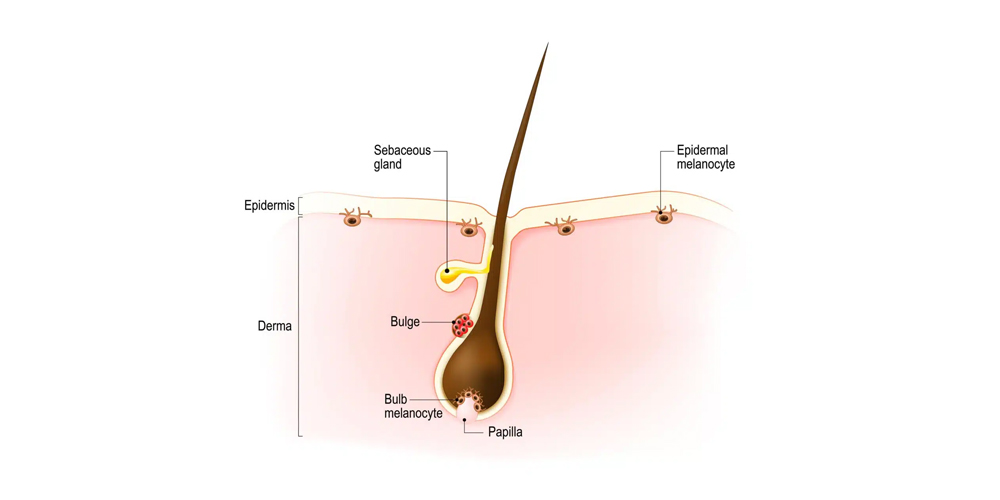
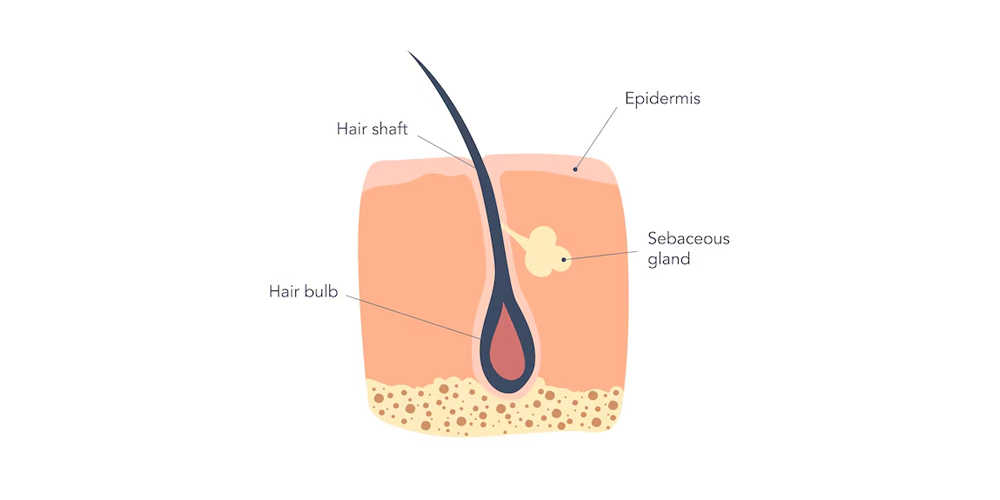
A hair follicle consists of several layers that work together to facilitate hair growth. At the core lies the dermal papilla, an accumulation of specialized cells that play an essential role in hair growth by providing nutrients. Surrounding the dermal papilla, you have the hair bulb, where the actual hair shaft begins its journey upward through the skin.
The follicle also comprises different types of cells, including epithelial cells that form the outer layer. This outer layer protects the inner workings of the follicle while playing a role in signaling pathways necessary for hair development and cycling.
Moreover, there are sebaceous glands associated with each follicle, producing sebum-a natural oil that helps to keep both the hair and skin moisturized. These glands highlight the interconnectedness of hair follicles with other skin structures, hinting at their wider significance beyond just hair production.
1.2. Types of Hair Follicles
Hair follicles can be categorized based on their location and the type of hair they produce. There are two primary types: the terminal hair follicles and the vellus hair follicles.
Terminal hair follicles give rise to thicker, longer hairs typically found on the scalp, face, and body. They are sensitive to hormonal changes and can undergo transformations due to factors like puberty or aging.
On the other hand, vellus hair follicles produce fine, soft hairs often called "peach fuzz." These hairs are less visible and tend to cover the majority of the human body, particularly in areas such as the arms and legs.
Understanding the differences between the types of hair follicles is essential for comprehending the biological processes involved in hair growth and loss. It provides insight into why certain treatments may work better for specific areas of the body.
1.3. The Growth Cycle of Hair Follicles
Every hair follicle goes through a distinct growth cycle, which consists of three main phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen.
Anagen is the growth phase when the hair is actively produced. Depending on genetics and other factors, this phase can last for several years, leading to long hair. Following the anagen phase is catagen, a transitional stage where hair stops growing and detaches from the dermal papilla. Finally, the telogen phase is the resting period when the hair remains in place until it eventually falls out, allowing for new growth to begin again.
Understanding this growth cycle is pivotal for anyone interested in hair health-whether you're looking into treatments for hair loss or ways to promote thicker, healthier hair.
2. The Role of Hair Follicles in Hair Growth
Hair follicles are central to the process of hair growth, serving as the birthplace for every strand we see on our bodies. This section explores the mechanisms by which hair follicles influence hair growth.
2.1. Cellular Dynamics in Hair Follicles
At the cellular level, hair follicles engage in a complex interplay of various cell types. Stem cells located at the base of the follicle play a critical role in generating new hair. These stem cells divide and differentiate into keratinocytes, the cells that eventually become the hair shaft.
Additionally, signaling molecules and hormones heavily influence this process. For example, androgens like testosterone can stimulate certain hair follicles while inhibiting others. This differential response explains why some individuals experience male or female pattern baldness as they age.
Moreover, research continues to discover new pathways and molecular signals that regulate this intricate process. Understanding these dynamics opens doors for innovative treatments aimed at rejuvenating hair growth and addressing hair loss conditions.
2.2. The Influence of Hormones
Hormones significantly influence hair follicle function. Conditions like androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as hereditary hair loss, exemplify the impact hormones have on hair follicles.
Androgens bind to receptors in hair follicles and modify the hair growth cycle, shortening the anagen phase. As a result, the hair becomes thinner and shorter over time. This hormonal effect varies across different areas of the body, explaining why some regions might maintain thicker hair while others do not.
Conversely, estrogen can encourage hair growth and prolong the anagen phase. This is why women often notice thicker hair during pregnancy or while on hormonal contraceptives.
Recognizing the hormonal influences at play allows for targeted approaches to managing hair loss, including hormone therapy or medications that block androgen receptors.
2.3. Environmental Factors Affecting Hair Growth
While hormonal balances are vital, external factors cannot be overlooked. Environmental influences-ranging from diet to stress levels-play an equally important role in hair follicle function and overall hair health.
For instance, poor nutrition can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, ultimately affecting hair growth. Biotin, zinc, and vitamins A and D all contribute significantly to maintaining healthy hair follicles.
Stress, too, has a profound impact. Chronic stress can trigger hair loss conditions such as telogen effluvium, where a larger-than-normal number of hair follicles enter the telogen phase simultaneously. This illustrates the necessity of holistic approaches to hair care that consider both internal and external factors.
3. Hair Follicles and Skin Health
Hair follicles do not merely serve the purpose of producing hair; they are integral components of skin health. This section focuses on the various ways hair follicles contribute to healthy skin.
3.1. The Protective Barrier
Hair follicles serve as part of the skin's barrier system. The presence of hair can protect the skin from sun exposure and physical irritants, acting almost like a shield. Additionally, the oils produced by sebaceous glands within the hair follicles help keep the skin moisturized.
This moisturizing factor is crucial; dry skin can lead to irritation, cracking, and increased vulnerability to infections. Thus, a healthy balance of oil production from the hair follicles contributes significantly to maintaining skin integrity.
3.2. The Immune System Interplay
Interestingly, hair follicles also participate in the immune response. The skin houses immune cells that can quickly respond to pathogens, and hair follicles are no exception.
These immune responses can be indirectly affected by the state of the hair follicle. For example, inflammation in the follicle can cause problems that manifest as conditions like acne or folliculitis, which occur when hair follicles become clogged and inflamed.
Keeping hair follicles healthy thus supports the broader immune function of the skin, shedding light on the critical connection between hair health and overall skin vitality.
3.3. Connection to Aging
As the body ages, hair follicles can lose their vitality, contributing to thinning hair and skin changes. The aging process causes a reduction in the number of active hair follicles and alters hormonal balances, resulting in the characteristic changes seen in older individuals.
This aging dynamic emphasizes the importance of caring for hair follicles throughout life. Regularly conditioning the scalp, using appropriate hair care products, and maintaining a balanced diet can help prolong follicular health.
4. The Future of Hair Follicle Research
As science advances, researchers continue to unveil the mysteries surrounding hair follicles. This section discusses emerging insights and future directions in hair follicle research.
4.1. Regenerative Medicine and Hair Follicles
One of the most exciting areas of research involves regenerative medicine and its potential applications for restoring hair. Scientists are investigating how to activate dormant hair follicles to promote regrowth in individuals suffering from hair loss.
Recent studies have explored stem cell therapies aimed at revitalizing hair follicles. By harnessing the body's innate healing capabilities, researchers hope to develop treatments that not only prevent hair loss but also reverse it entirely.
4.2. Genetic Studies and Personalized Treatments
Genetic research is paving the way for personalized treatment plans. Understanding one's genetic predisposition can inform specific strategies to manage hair loss effectively.
For instance, identifying variations in genes related to hair follicle cycling could lead to customized topical solutions or systemic treatments tailored to an individual's unique physiology.
The future of hair restoration looks promising, as genetic insights allow for more accurate diagnoses and targeted approaches.
4.3. Psychosocial Implications
While the science of hair follicles is essential, the psychosocial implications of hair health can’t be ignored. Society often attaches significant meaning to hair, impacting self-esteem and identity.
Ongoing research aims to understand how conditions like alopecia areata affect psychological well-being, highlighting the need for comprehensive care that includes mental health support alongside medical interventions.
Conclusion
In summary, the question What is a Hair Follicle transcends mere anatomical interest; it expands into the realms of health, biology, and psychology. From their intricate structure and multifaceted functions to their profound significance in our lives, hair follicles are remarkable organs deserving of our attention and understanding. As research continues to evolve, so does our comprehension of these tiny yet powerful entities, opening doors to innovative treatments and deeper insights into our health and well-being. So, whether you're dealing with hair loss or simply curious about your own hair, remember the crucial role hair follicles play in shaping not just our appearance but our overall health and sense of self.
LATEST POSTS








