What Can I Do To Stop My Alopecia Areata Symptoms?
Alopecia areata (AA) can be a challenging and distressing condition, characterized by patches of hair loss on the scalp, face, and body. This autoimmune disease affects around 2% of the population at any age, making it a topic that resonates with many individuals looking for ways to manage their symptoms. The heart of the problem lies in a miscommunication from the immune system, which mistakenly targets healthy hair follicles as threats. While there is currently no cure for alopecia areata, various treatment options can help control its progression and, in some cases, even promote regrowth. This article aims to provide insights into managing alopecia areata symptoms, exploring different approaches, treatments, lifestyle changes, and emotional support strategies.
1. Understanding Alopecia Areata: The Immune System Connection
To find effective solutions for managing alopecia areata, it's essential to understand the role of the immune system in this complex condition.
1.1. The Immune System's Role
Your immune system functions like a diligent soldier, guarding against harmful invaders such as viruses and bacteria. However, in the case of alopecia areata, this protective mechanism goes awry. The body's defense system, instead of distinguishing between friends and foes, starts attacking healthy hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss.
This miscommunication within the immune system may stem from genetic predispositions or environmental factors that trigger an autoimmune response. These triggers could include stressful life events, infections, or other underlying health issues. Understanding this misdirected response is crucial in identifying potential treatment options and lifestyle adjustments that might mitigate symptoms.
1.2. Types of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata manifests in several forms:
- Alopecia Areata: Characterized by coin-sized bald patches.
- Alopecia Totalis: A more severe form where all hair on the scalp is lost.
- Alopecia Universalis: The most extreme variant, resulting in complete hair loss across the entire body.
Recognizing the type of alopecia areata one is dealing with can guide treatment choices and expectations.
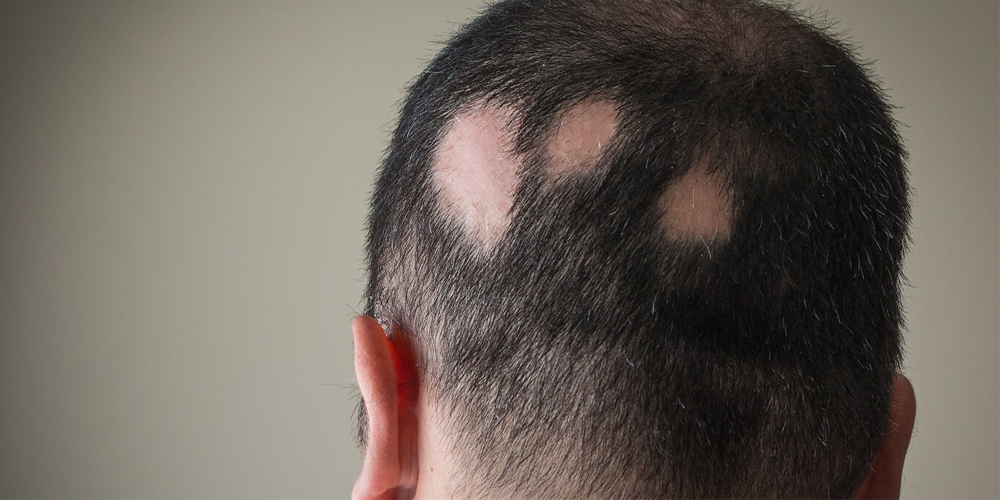
1.3. The Psychological Impact
The repercussions of alopecia areata extend beyond physical symptoms; they often affect mental health and self-esteem. Experiencing sudden hair loss can lead to feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and isolation. It’s essential to acknowledge these emotions while seeking paths toward acceptance and coping mechanisms to enhance overall well-being.
2. Conventional Treatments for Alopecia Areata
While there isn’t a definitive cure for alopecia areata, a variety of conventional treatment options exist to manage the symptoms effectively.
2.1. Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids, like clobetasol propionate, frequently serve as a first-line treatment for alopecia areata.
These creams or ointments target specific areas of hair loss, helping suppress the local immune response and reducing inflammation. Many patients experience success with these topical treatments, leading to regrowth in affected areas.
However, long-term use carries potential side effects, including skin thinning, acne, and stretch marks. It’s vital to work closely with a dermatologist to minimize risks while maximizing benefits.
2.2. Corticosteroid Injections
In cases involving larger patches of hair loss, corticosteroid injections directly into the scalp may be recommended.
This method can sometimes yield quicker results than topical applications, encouraging hair regrowth in more substantial areas. The injection process can be daunting for some due to the pain involved, but many individuals find the trade-off worth it for the potential results.
On the flip side, localized skin changes at the injection site may occur, so it’s essential to discuss the pros and cons with a healthcare professional.
2.3. Phototherapy: Harnessing Light for Growth
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the scalp to ultraviolet (UV) light. This method can stimulate hair growth in some individuals with alopecia areata.
Although it requires multiple sessions and careful monitoring to avoid skin damage, phototherapy shows promise when used alongside other treatments. For those struggling with extensive hair loss, it may offer a viable option for regaining confidence and promoting regrowth.
2.4. Immunosuppressants: A Broader Approach
More severe cases of alopecia areata may necessitate immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or cyclosporine.
These oral medications regulate the immune system more comprehensively, which can be beneficial for individuals who have not responded to topical treatments. However, the potential for serious side effects means that these drugs require close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
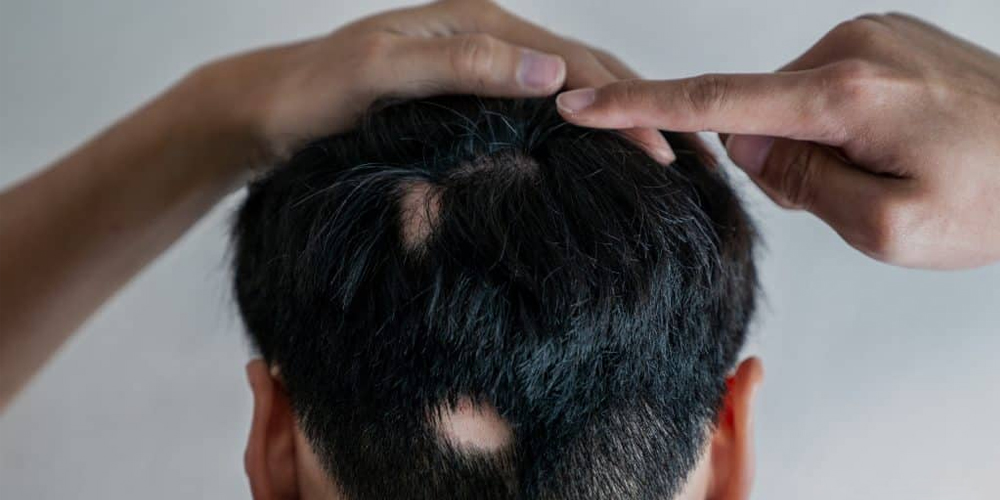
2.5. Other Medications Worth Considering
In addition to the aforementioned treatments, other medications may also offer benefits for individuals with alopecia areata:
- Minoxidil: Typically used for androgenic alopecia (male pattern baldness), minoxidil can stimulate hair growth and may benefit those with AA as well.
- Oral Minoxidil: An emerging option that provides a systemic approach to treatment.
- Antralin: A topical solution that promotes faster hair growth and helps enhance the effectiveness of other treatments.
Each medication comes with its unique set of advantages and potential risks, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment plans based on individual needs and responses.
3. Alternative Therapies and Lifestyle Modifications
Many individuals seek alternative therapies and lifestyle modifications to complement traditional treatments for alopecia areata. While scientific evidence may be limited, these strategies can still provide meaningful support for managing symptoms.
3.1. Dietary Adjustments
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in overall health and well-being, making dietary changes an interesting avenue to explore. Although specific food groups haven’t been proven to cure alopecia areata, many find adopting a nutrient-rich diet helpful.
A focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can support the immune system. Some report positive effects from eliminating processed foods or allergens, suggesting that a tailored diet could potentially impact symptoms.
3.2. Supplements for Hair Health
Certain supplements, such as zinc, biotin, and iron, are often recommended for individuals with alopecia areata.
While they might support hair health, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen. Some supplements can interact with medications or lead to adverse effects when taken inappropriately.
3.3. Reducing Stress: A Key Component
Stress has been linked to worsening autoimmune conditions, including alopecia areata.
Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can create a conducive environment for healing. These practices help foster a sense of calm and balance, both of which may play important roles in managing autoimmune responses.
3.4. The Power of Acupuncture
Some studies suggest that acupuncture may encourage hair regrowth in individuals with alopecia areata.
By targeting specific points on the body, acupuncture seeks to improve circulation and reduce inflammation. Though more research is needed to validate its efficacy, many people appreciate the relaxation and holistic benefits it offers.
3.5. Embracing Holistic Practices
Ultimately, embracing a holistic approach that combines traditional treatment with alternative therapies can pave the way for improved management of alopecia areata. Recognizing the interconnectedness of physical and emotional well-being is crucial in navigating this complex condition.
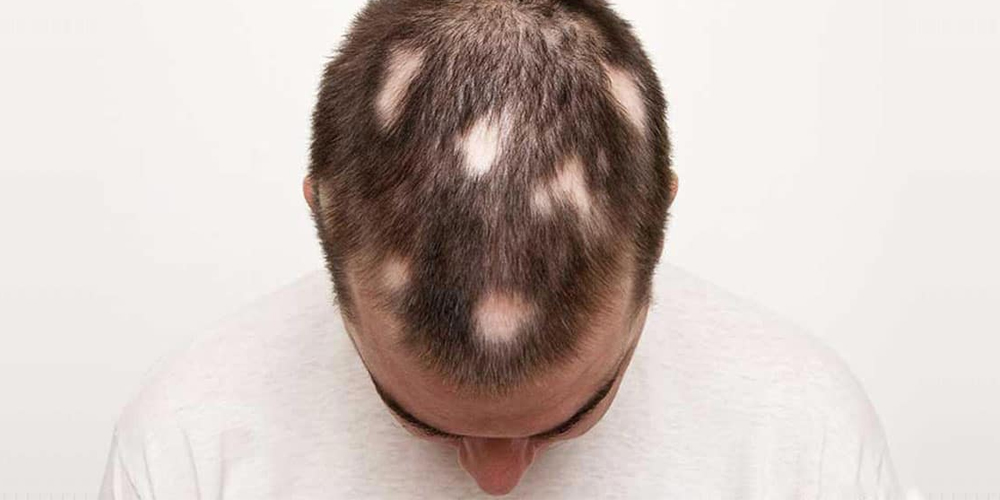
4. Finding Support and Managing Emotional Challenges
Living with alopecia areata poses unique emotional and psychological challenges. Addressing these aspects is just as important as focusing on physical treatment options.
4.1. Building Connections: Support Groups
Connecting with others who share similar experiences can be immensely valuable.
Online forums, local support groups, and social media can provide spaces for sharing struggles, seeking advice, and fostering community. Knowing you’re not alone in your journey can alleviate feelings of isolation and fear.
4.2. Seeking Professional Guidance
For some, the emotional toll of alopecia areata may become overwhelming, impacting daily life and relationships. Seeking help from a therapist or counselor can be a constructive step toward finding coping strategies and enhancing resilience.
Professional guidance allows individuals to address underlying emotions, build self-esteem, and develop tools for navigating the ups and downs of living with hair loss.
4.3. Focusing on Strengths and Passions
It’s crucial to remind oneself that alopecia areata doesn’t define personal identity or self-worth. Shifting the focus from hair loss to strengths and interests can promote positivity and fulfillment. Engaging in hobbies, pursuing careers, and spending time with loved ones can create a sense of normalcy amid challenges.
4.4. Embracing Self-Care Practices
Self-care is paramount for managing emotional health. Activities such as exercise, creative pursuits, and mindfulness techniques can cultivate a sense of well-being and joy. Ensuring you dedicate time to nurture yourself physically, mentally, and emotionally fosters resilience against the challenges posed by alopecia areata.
5. Can a Hair Transplant Cure Alopecia Areata?
A hair transplant is rarely recommended for people with alopecia areata. This is because your autoimmune system will continue to attack your hair follicles even if they are in a new location. Therefore, if you transplanted hairs into the bald patches, it’s likely that they will fall out just like the hair that was there before. This will also speed up the hair loss process because you are moving unaffected hair into an area where your body has been attacking the hair follicles.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata can present significant hurdles, affecting both physical appearance and emotional well-being. While there is no cure, a wide range of treatment options-both conventional and alternative-exists to help manage symptoms and promote hair regrowth.
Understanding the root causes of alopecia areata, exploring various therapeutic approaches, and addressing emotional health are vital steps. By collaborating with healthcare professionals and building supportive networks, individuals can navigate the complexities of this condition more effectively. Remember, you are not alone on this journey, and together, we can continue to seek understanding and empowerment in the face of alopecia areata.
LATEST POSTS








