Scalp Fungus and Hair Loss
Scalp Fungus and Hair Loss are two interconnected issues that can significantly impact an individual's physical appearance and emotional well-being. The presence of fungal infections on the scalp can lead to various forms of hair loss, making it essential to understand the relationship between these conditions. This article delves into the intricacies of scalp fungus, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the impact it has on hair loss.
1. Understanding Scalp Fungus
Scalp fungus, commonly referred to as a fungal infection, is primarily caused by dermatophytes, which are a group of fungi that thrive in warm and moist environments. When these fungi invade the scalp, they can disrupt the normal growth cycle of hair follicles, leading to hair thinning or bald patches.
Fungal infections can manifest in several forms, including ringworm (tinea capitis), seborrheic dermatitis, and candidiasis. Each type presents unique challenges and requires specific approaches for effective management.
1.1. What Causes Scalp Fungus?
The causes of scalp fungus are diverse and often interrelated. Understanding these factors can help individuals avoid situations that foster the growth of these harmful fungi.
Environmental Factors: The environment plays a significant role in the development of scalp fungus. Warm, humid climates create ideal conditions for fungi to flourish. Excessive sweating, inadequate hygiene, or shared personal items like hairbrushes and hats can further exacerbate the problem.
Personal Habits: Certain personal habits can contribute to the prevalence of scalp fungus. Individuals who frequently wear tight hairstyles or hats may experience increased moisture retention on the scalp, creating an optimal breeding ground for fungi. Additionally, poor nutrition and stress can weaken the immune system, making it easier for fungal infections to take hold.
Underlying Health Conditions: Some underlying health issues may predispose individuals to scalp fungus. For instance, those with compromised immune systems, such as people living with diabetes or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk. Furthermore, hormonal imbalances can also play a role in the occurrence of these infections.
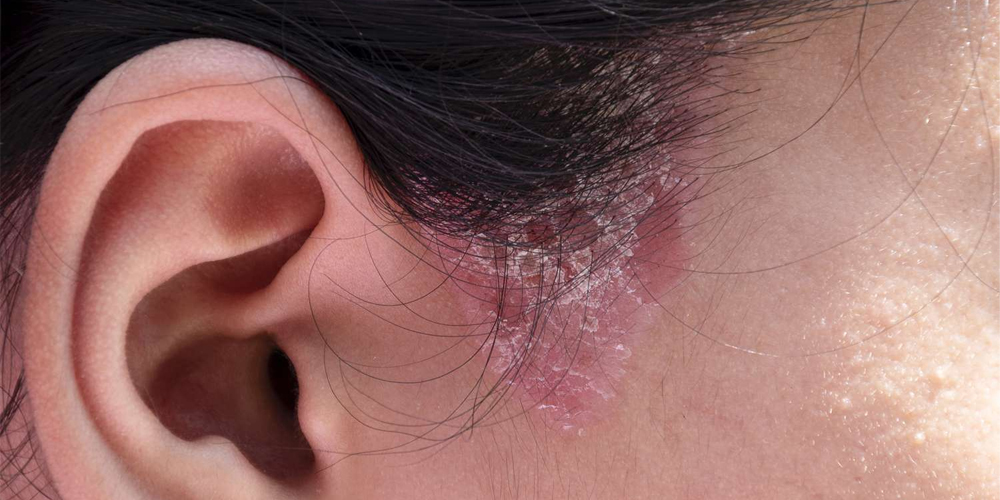
1.2. Symptoms of Scalp Fungus
Identifying the symptoms of scalp fungus is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Some common signs include:
Itching and Inflammation: One of the most common symptoms of scalp fungus is persistent itching that may accompany redness and inflammation. Affected individuals may experience discomfort, leading to increased scratching, potentially worsening the condition.
Hair Loss and Bald Patches: As the infection progresses, it may cause hair loss, resulting in noticeable bald patches on the scalp. The hair may become brittle and break off easily, making it challenging to maintain healthy hair.
Scaly Patches and Crusts: Infected areas may develop scaly patches or crusts that resemble dandruff but require different treatment methods. These patches can be unsightly and may even contribute to social anxiety for some individuals.
1.3. Types of Scalp Fungus
Several types of scalp fungus exist, each with distinct characteristics and implications for hair loss.
Tinea Capitis: Tinea capitis, commonly known as ringworm of the scalp, is one of the most prevalent types of fungal infections affecting the hair and scalp. It presents as circular patches of hair loss accompanied by scaly skin. If not treated promptly, this condition can lead to permanent hair loss in the affected areas.
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by red, flaky patches on the scalp and can cause hair thinning. While not exclusively a fungal infection, Malassezia yeast contributes to its development. This condition may be chronic and recurrent, requiring ongoing management to keep symptoms under control.
Candidiasis: Candidiasis is another form of scalp fungus caused by Candida yeast. Although it is less common than tinea capitis, it can still lead to hair loss if left untreated. Symptoms often include redness, itching, and thick white patches.
2. Impact of Scalp Fungus on Hair Loss
The connection between scalp fungus and hair loss is both direct and indirect, as fungal infections can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle. Understanding how these two issues intertwine can provide valuable insights into prevention and treatment strategies.
2.1. Direct Hair Follicle Damage
Scalp fungus can directly damage hair follicles by invading them and causing inflammation. This inflammation prevents normal hair growth, leading to temporary or even permanent hair loss in severe cases.
When fungi penetrate the hair follicles, they can also trigger an immune response that further damages the follicle structure. This inflammation can lead to scarring, making it difficult for new hair to grow back even after the infection is cleared.
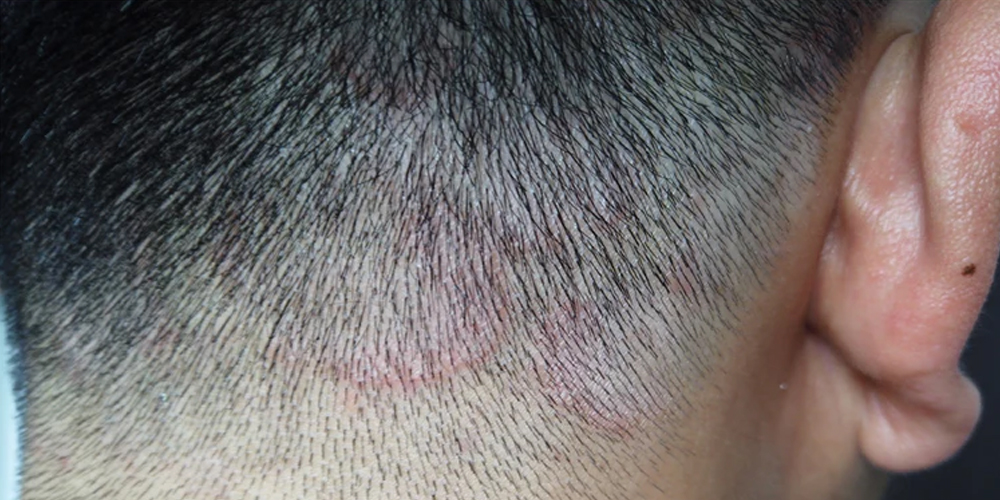
2.2. Indirect Psychological Effects
Beyond the physical implications, scalp fungus and hair loss can lead to psychological distress. Individuals suffering from visible hair loss often experience decreased self-esteem and social withdrawal. The stigma associated with hair loss can be profound, creating feelings of embarrassment and inadequacy.
This psychological burden may result in behaviors that exacerbate the situation, such as excessive scratching, which can worsen scalp irritation and prolong the healing process. It is crucial to address not only the physical symptoms of scalp fungus but also the emotional toll it takes on affected individuals.
2.3. Treatment Options for Scalp Fungus
Addressing the issue of scalp fungus requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive therapies.
Topical Antifungals: Over-the-counter antifungal shampoos and creams are often the first line of defense against scalp fungus. Ingredients like ketoconazole, clotrimazole, and selenium sulfide have proven effective in eliminating fungal infections and promoting scalp health. For more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe stronger topical medications or oral antifungals. It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations to ensure effective treatment and minimize the risk of recurrence.
Lifestyle Changes: Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing scalp fungus. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as regularly washing hair and using clean hair accessories, is crucial. Avoiding tight hairstyles and keeping the scalp dry can also help prevent fungal growth. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health and boosts the immune system, making it more resilient against infections.
Emotional Support: Seeking emotional support during this challenging time is vital. Talking to friends or joining support groups can alleviate feelings of isolation and shame. Therapy may also be beneficial for those struggling to cope with the psychological aspects of hair loss.
Conclusion
Addressing scalp fungus and hair loss requires a comprehensive understanding of their interconnected nature. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and impact of scalp fungus, individuals can take proactive steps towards effective treatment and management.
Through targeted interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support, it is possible to combat the effects of scalp fungus, promote healthy hair growth, and regain self-confidence. Ultimately, raising awareness about these issues can empower individuals to seek help when needed and foster healthier scalps for themselves and others. By understanding and addressing scalp fungus effectively, we can pave the way for healthier hair and a better quality of life.
LATEST POSTS








