DHT: Why This Hormone Is Wreaking Havoc on Your Hair Follicles
Dihydrotestosterone, commonly known as DHT, is a hormone that can significantly impact hair health, leading to distressing conditions such as hair loss and baldness. While many people may initially overlook the role of hormones in their hair journey, understanding how DHT functions and its effects on hair follicles is crucial for anyone experiencing thinning hair or baldness. This article delves deep into the world of DHT, exploring its implications for both men and women and providing insights into effective management strategies.
1. Understanding DHT and Its Role in Hair Loss
DHT is an androgen, a type of hormone that contributes to the development of male characteristics, but it also has profound effects on hair follicles. The interaction between DHT and these follicles initiates a cascade of biochemical responses that can lead to hair loss. By examining this relationship closely, we can uncover the mechanisms by which DHT wreaks havoc on our hair.
1.1. The Biochemical Mechanisms Behind DHT's Impact
To truly understand how DHT affects hair follicles, it's essential first to look at the underlying biochemical interactions that occur when DHT binds to androgen receptors within the follicles.
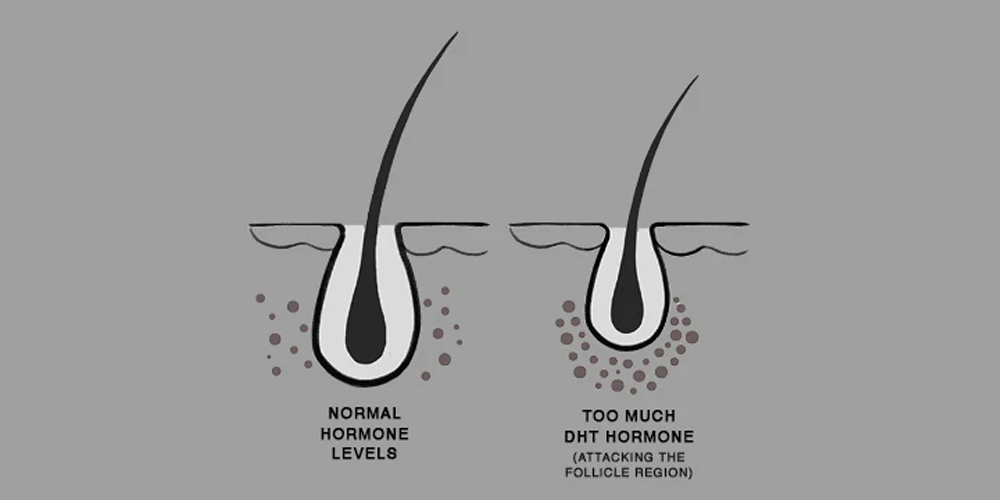
DHT is derived from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. Once produced, DHT can bind to androgen receptors located in hair follicles, triggering several changes that contribute to hair loss.
The binding initiates follicle miniaturization, where the size of the hair follicle decreases over time. Miniaturization leads to thinner, shorter hair strands, which makes them more prone to falling out. Moreover, the presence of DHT shortens the anagen phase-the growth phase of the hair cycle-resulting in hair not reaching its full potential length before transitioning to the telogen phase, the resting phase. As a result, there is an increased rate of hair shedding.
Additionally, the prolonged exposure to DHT leads to follicle atrophy, wherein the follicles become progressively incapable of producing new hair. The end result is a distinct reduction in hair density and ultimately, permanent baldness.
1.2. The Genetic Component of DHT-Related Hair Loss
While DHT plays a pivotal role in hair loss, the genetic predisposition of an individual significantly influences susceptibility to DHT's effects.
Each person’s unique genetic makeup determines how their body responds to DHT. Variations in the androgen receptor gene can increase sensitivity to DHT, making certain individuals more vulnerable to hair loss. In other cases, some people may inherit variations that enhance the activity of enzymes responsible for converting testosterone into DHT, further exacerbating hair loss issues.
Moreover, individual hair follicles exhibit varying sensitivity levels to DHT. Some follicles are inherently more reactive to the hormone, resulting in hair loss even at lower levels of DHT. Thus, genetics play a key role in whether someone experiences hair loss related to this potent androgen.
1.3. DHT and Gender Differences in Hair Loss
Although DHT is often associated with male pattern baldness, its role in hair loss is not limited to men. Women are also affected, albeit differently.
In males, DHT contributes to a characteristic pattern of hair loss, typically starting with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown of the head. This progression can be tracked using the Norwood-Hamilton scale, which categorizes stages of male pattern baldness.
Conversely, female pattern hair loss presents itself as diffuse thinning across the scalp rather than distinct patches. Women tend to have lower levels of DHT compared to men, but those with a family history of androgenetic alopecia are still at risk. Hormonal fluctuations during significant life events like menopause can elevate DHT levels, leading to hair loss in women as well.
2. Strategies for Managing DHT-Related Hair Loss
Given the detrimental effects of DHT on hair follicles, exploring effective management options is essential for those suffering from hair loss. Various approaches can help mitigate the impacts of DHT and potentially stimulate hair regrowth.
2.1. Topical Treatments and Medications
When it comes to managing DHT-related hair loss, topical treatments are among the most accessible forms of intervention. Minoxidil and finasteride are two popular medications with proven efficacy.
Minoxidil is available without a prescription and works by improving blood flow to hair follicles, which may help counteract the effects of DHT. It widens blood vessels in the scalp, potentially allowing for better nutrient delivery to the follicles. Some studies suggest that it may also block DHT action, although the precise mechanism remains under investigation.
Finasteride, on the other hand, is a prescription medication that tackles the root problem by inhibiting the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride can effectively slow down and even reverse hair loss in men. However, it’s essential to note that finasteride may come with potential side effects-including sexual dysfunction-which should be carefully discussed with a healthcare provider.

2.2. Lifestyle Modifications for Hair Health
In addition to medical therapies, lifestyle modifications can play a critical role in managing hair loss related to DHT. These include dietary changes, stress management techniques, and avoiding harsh chemicals.
A diet rich in antioxidants, proteins, and vitamins can support overall hair health. Nutrients such as biotin, zinc, and vitamins A and E can promote healthier hair follicles and combat oxidative stress, which may exacerbate hair loss.
Furthermore, chronic stress can trigger or worsen hair loss. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time outdoors can help manage stress levels. Reducing stress can positively impact overall health and may also improve hair quality.
Lastly, avoiding harsh chemicals found in hair styling products is vital. Certain dyes and styling agents can irritate the scalp and damage delicate hair follicles. Opting for gentler, more natural alternatives could benefit both hair and scalp health.
2.3. Surgical Interventions: Hair Transplantation
For individuals with significant hair loss, surgical interventions may provide a lasting solution. Two primary methods for hair transplantation exist: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
FUT involves harvesting strips of hair-bearing skin from the back of the head and transplanting the follicles into balding areas. This method allows for the transplantation of multiple follicles simultaneously but may leave a linear scar.
Conversely, FUE entails extracting individual hair follicles from the donor site and implanting them into balding areas. While this method is less invasive and leaves minimal scarring, it can be more time-consuming.
Both techniques offer a permanent solution to hair loss but come with considerations regarding cost and recovery time. Individuals interested in surgical options should consult with qualified professionals to assess their suitability for these procedures.
2.4. Innovative Therapies: PRP and Low-Level Laser Therapy
In addition to traditional treatment methods, innovative therapies such as Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injections and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) are emerging as promising options for tackling hair loss.
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting it into the scalp. The growth factors contained in the platelet-rich plasma can stimulate hair follicles, potentially promoting hair regrowth. Many patients report positive results, particularly when used alongside other treatment modalities.
Low-level laser therapy employs specific wavelengths of light to stimulate hair follicles. Research suggests that LLLT may enhance blood flow and cellular activity, promoting hair growth and improving hair density. This non-invasive treatment can be performed in-office or with at-home devices, making it an appealing option for many seeking to combat hair loss.
Conclusion
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) plays a significant role in hair loss through its interaction with hair follicles, leading to miniaturization and eventual baldness. Understanding how DHT operates and the genetic factors contributing to individual susceptibility can aid in developing effective management strategies against hair loss.
Though confronting hair loss can be daunting, a variety of treatment options are available-from topical medications to lifestyle modifications, surgical interventions, and innovative therapies. Consulting with a dermatologist or hair loss specialist is crucial for assessing the cause of hair loss and creating a personalized management plan that considers individual needs and preferences. With the right approach, you can take proactive steps towards restoring your hair's health and vitality.
LATEST POSTS








