Why Is Pattern Baldness More Common In Men?
The sight of a receding hairline or a shiny scalp isn't just a cosmetic concern; it's a common experience for millions of men worldwide. While hair loss can affect both genders, pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, disproportionately impacts men. This phenomenon raises an important question: Why is pattern baldness more common in men? The answer lies in a complex interplay of genetics, hormones, and environmental factors that converge to create this widespread condition. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects contributing to male pattern baldness, exploring its genetic underpinnings, hormonal influences, the lifecycle of hair, environmental impacts, psychological effects, and treatment options available.
1. Why Is Pattern Baldness More Common In Men? - The Role of Genetics
Genetics plays a pivotal role in determining an individual's susceptibility to pattern baldness. Just like you inherit your eye color or height, the predisposition to hair loss is passed down through generations. Understanding the genetic factors involved can shed light on why some men experience significant hair loss while others maintain a full head of hair well into their later years.
1.1. Inherited Traits and Genetic Markers
Research has identified specific genes associated with hair growth and loss. These genes are linked to androgen receptor sensitivity, which is crucial in the development of androgenetic alopecia. The inheritance of these traits often follows a polygenic pattern, meaning multiple genes contribute to the likelihood of developing pattern baldness.
Men who have a family history of hair loss, particularly on the paternal side, are at a higher risk of experiencing similar issues. If a father or grandfather experienced pattern baldness, it increases the chances that subsequent generations may face the same fate. This hereditary aspect underscores the importance of understanding one's family background when assessing the risk of hair loss.
1.2. The Role of Androgen Receptors
Androgen receptors are proteins that bind to hormones like testosterone and DHT (dihydrotestosterone). The sensitivity of these receptors can vary significantly among individuals, influencing how they respond to hormonal changes. Men with highly sensitive androgen receptors are more likely to experience hair miniaturization and loss when exposed to elevated levels of DHT.
Studies have shown that certain genetic variations can enhance the expression of androgen receptors in hair follicles, making them more susceptible to the effects of DHT. This genetic predisposition is a critical factor in understanding why pattern baldness is more prevalent in men than women, as men typically have higher levels of testosterone and, consequently, DHT.
1.3. The Complexity of Genetic Interactions
While specific genes play a significant role in hair loss, the interaction between these genes and environmental factors adds another layer of complexity. For instance, lifestyle choices, stress levels, and overall health can influence how genetic predispositions manifest. Even if a man carries the genetic markers for pattern baldness, external factors can either exacerbate or mitigate the condition's progression.
This intricate relationship between genetics and environment highlights the need for a comprehensive approach to understanding and addressing pattern baldness. By recognizing the genetic components, men can better navigate their hair loss journey and explore potential interventions.
2. Hormones: The Androgen Connection
While genetics set the stage for pattern baldness, hormones act as the director in this unfolding drama. The primary culprit behind male pattern baldness is the male hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. Understanding the role of hormones in hair loss provides valuable insights into why men are more affected by this condition.
2.1. The Production of DHT
DHT is produced from testosterone through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. This conversion process occurs primarily in the hair follicles, prostate, and adrenal glands. In men, higher testosterone levels naturally lead to increased production of DHT. As a result, men are more prone to the effects of this potent androgen, especially during puberty when testosterone levels surge.
DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, initiating a series of events that ultimately lead to hair miniaturization and shedding. This binding process disrupts the normal hair growth cycle, causing follicles to shrink and produce thinner, weaker hairs over time.
2.2. Sensitivity to DHT
Not all men respond equally to DHT. The sensitivity of hair follicles to this hormone varies significantly among individuals. Some men may experience rapid hair loss due to heightened sensitivity, while others may only see gradual thinning. This variability can be attributed to genetic factors, including the presence of specific androgen receptor variants that increase follicle sensitivity to DHT.
Understanding this sensitivity is crucial for developing effective treatments for pattern baldness. By targeting the underlying hormonal imbalances, men can take proactive steps to manage their hair loss and potentially reverse its effects.
2.3. Hormonal Changes Over Time
As men age, hormonal fluctuations can further exacerbate the effects of DHT on hair follicles. Testosterone levels typically decline with age, but the ratio of testosterone to DHT can shift, leading to increased DHT activity relative to available testosterone. This imbalance can accelerate hair loss in men who are already genetically predisposed to pattern baldness.
Additionally, other hormonal factors, such as thyroid hormones and cortisol, can influence hair health. Chronic stress, for example, can elevate cortisol levels, which may suppress hair growth and contribute to hair loss. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of hormonal influences is essential for understanding the complexities of pattern baldness.
3. The Lifecycle of Hair: A Battle of Cycles
To comprehend pattern baldness fully, one must understand the hair growth cycle. Hair follicles undergo three distinct phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). Disruptions in this cycle can lead to hair thinning and loss, particularly in men affected by androgenetic alopecia.
3.1. The Phases of Hair Growth
The anagen phase is the active growth stage, where hair follicles produce new cells and lengthen the hair strand. This phase typically lasts several years, allowing for the growth of long, healthy hair. Following the anagen phase, hair enters the catagen phase, a brief transitional period where growth slows, and the follicle begins to shrink.
Finally, hair enters the telogen phase, during which the follicle remains dormant, and hair may eventually fall out. Under normal circumstances, hair follicles cycle through these phases seamlessly. However, DHT disrupts this process, leading to shorter anagen phases and prolonged telogen phases.
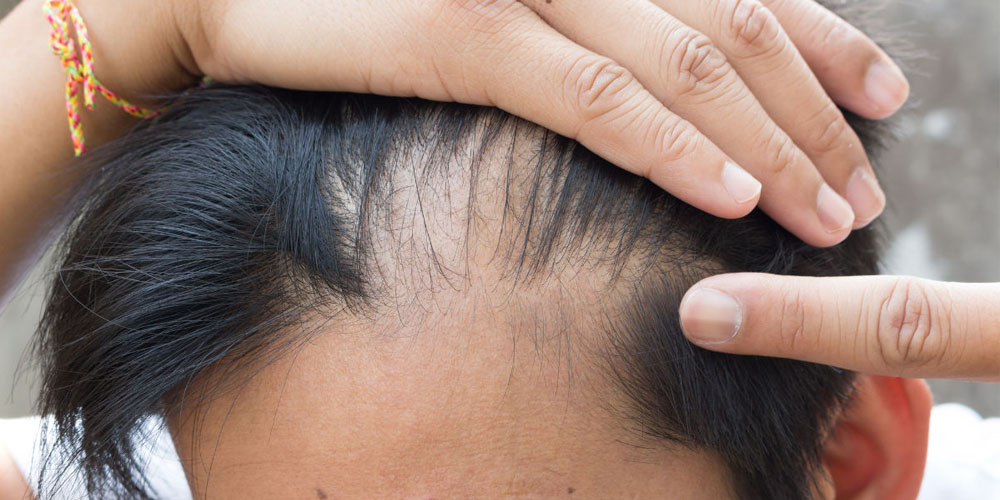

3.2. The Impact of DHT on Hair Follicles
DHT's influence on hair follicles is profound. As DHT binds to androgen receptors, it triggers a cascade of events that cause hair follicles to shrink and produce thinner, weaker hairs. Over time, this miniaturization results in a noticeable reduction in hair density and volume.
In the early stages of hair loss, follicles may still cycle through anagen, catagen, and telogen phases, albeit with shortened durations. However, as DHT's effects intensify, follicles become progressively smaller and less capable of producing strong, healthy hair. Eventually, they may enter a persistent telogen phase, where hair growth essentially ceases.
3.3. The Psychological Effects of Hair Loss
The impact of disrupted hair growth cycles extends beyond physical appearance. Many men experience emotional distress and anxiety related to hair loss, leading to decreased self-esteem and confidence. The societal emphasis on a full head of hair can exacerbate these feelings, making it essential to address the psychological aspects of pattern baldness alongside its biological causes.
Understanding the hair growth cycle and the role of DHT can empower men to seek appropriate treatments and support. By recognizing that hair loss is a complex interplay of factors, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their overall well-being.
4. The Environmental Impact: Beyond Biology
While genetics and hormones play a starring role in pattern baldness, environmental factors can act as supporting actors, influencing the progression of hair loss. Stress, pollution, poor diet, and lifestyle choices can all contribute to hair thinning and loss, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to hair health.
4.1. The Role of Stress
Chronic stress is a significant contributor to hair loss. When the body experiences prolonged stress, it releases cortisol, a hormone that can suppress hair growth and shorten the anagen phase. Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones necessary for healthy hair growth, leading to increased shedding and thinning.
Moreover, stress can trigger conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair follicles prematurely enter the telogen phase, resulting in temporary hair loss. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and mindfulness practices can help mitigate its impact on hair health.
4.2. Pollution and Its Effects
Environmental pollutants, such as particulate matter and chemicals, can damage hair follicles and hinder hair growth. Exposure to air pollution has been linked to increased hair shedding and reduced hair density. Pollutants can infiltrate the scalp and disrupt the natural balance of oils and nutrients necessary for healthy hair.
Maintaining a clean and healthy environment is essential for promoting hair health. Regularly washing the scalp and protecting it from harmful pollutants can help preserve hair quality and prevent premature loss.
4.3. Nutritional Deficiencies and Lifestyle Choices
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for maintaining healthy hair. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamins and minerals like biotin, zinc, and vitamin D, can weaken hair follicles and contribute to thinning. Men should prioritize a diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support hair health.
Lifestyle choices, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can also negatively impact hair growth. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the scalp and depriving hair follicles of oxygen and nutrients. By adopting healthier habits and making conscious dietary choices, men can significantly contribute to overall hair health.
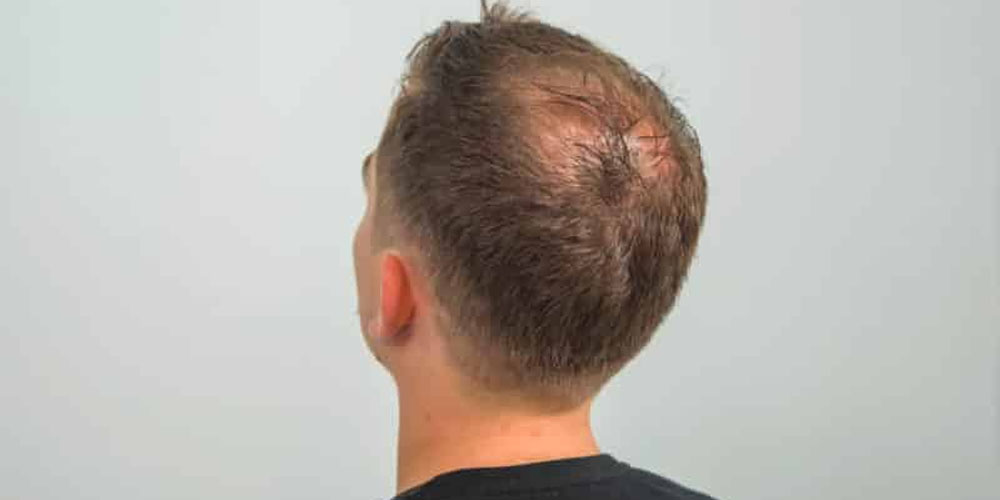
5. More Than Just a Cosmetic Issue
The psychological impact of hair loss cannot be underestimated. For many men, the experience of losing their hair goes beyond mere aesthetics; it can deeply affect self-esteem, social interactions, and mental well-being. Understanding the emotional ramifications of pattern baldness is crucial for fostering resilience and acceptance.
5.1. Self-Perception and Identity
Hair often plays a significant role in shaping a person's identity and self-perception. For men, a full head of hair is often associated with youthfulness, vitality, and attractiveness. As hair begins to thin or recede, many men experience feelings of self-consciousness and insecurity. This shift in self-image can lead to anxiety and depression, affecting various aspects of life, including relationships and career opportunities.
5.2. Social Stigma and Pressure
Societal norms and expectations surrounding masculinity and appearance can exacerbate the emotional toll of hair loss. Men may feel pressured to conform to ideals of attractiveness, leading to feelings of inadequacy and isolation. The stigma associated with baldness can deter men from seeking support or discussing their experiences openly.
Creating a supportive environment that encourages open dialogue about hair loss can help alleviate some of the emotional burdens associated with this condition. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can foster a sense of community and understanding.
5.3. Building Resilience and Acceptance
Navigating the challenges of hair loss requires patience and self-compassion. Embracing a holistic approach that encompasses both medical treatment and self-care can empower men to build resilience and acceptance. Seeking professional guidance, whether through therapy or support groups, can provide valuable tools for coping with the emotional aspects of hair loss.
Ultimately, recognizing that hair loss is a common experience shared by many can help men reframe their perspective and focus on their unique qualities beyond physical appearance. Building confidence and self-worth independent of hair can lead to greater overall well-being.
6. Combating Hair Loss: The Treatment Landscape
Despite its complex nature, pattern baldness can be managed effectively. Various treatment options are designed to address different stages of hair loss and individual needs. Understanding the available options can empower men to make informed decisions about their hair health.
6.1. Medications for Hair Loss
Several medications are commonly prescribed to combat hair loss. Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a topical solution available over-the-counter that works by increasing blood flow to the scalp and stimulating hair growth. It is suitable for both men and women and can be applied directly to the affected areas.
Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral medication that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, slowing down the progression of hair loss. It is specifically approved for use in men and has shown promising results in clinical studies. However, potential side effects should be discussed with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
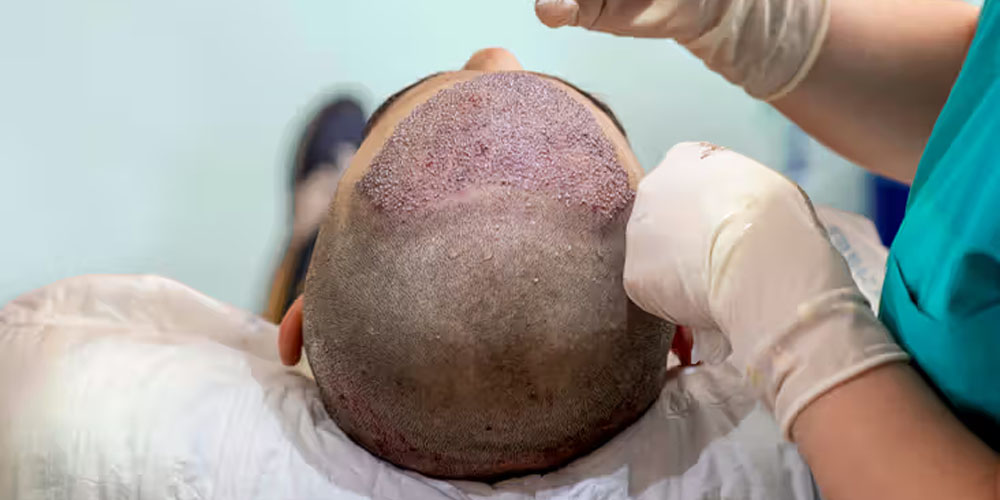
6.2. Surgical Options: Hair Transplant Surgery
For those seeking a more permanent solution, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from one area of the scalp to a balding area, resulting in natural-looking hair restoration. While hair transplant surgery can yield satisfying results, it is invasive, costly, and may require multiple sessions for optimal outcomes.
6.3. Alternative Therapies: Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is an emerging treatment option that stimulates hair follicles and promotes hair growth. Although its effectiveness is still under investigation, some studies suggest that LLLT may improve hair density and thickness. Men considering this option should consult with a qualified professional to determine its suitability for their specific situation.
6.4. Lifestyle Modifications for Hair Health
In addition to medical treatments, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to overall hair health. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and avoiding smoking. Regular exercise can also promote circulation and improve overall well-being, benefiting hair health.
6.5. Embracing a Holistic Approach
Combating hair loss requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition. Combining medical treatments with lifestyle modifications and emotional support can empower men to navigate the challenges of pattern baldness effectively.
By embracing a holistic approach, individuals can take control of their hair health and build resilience in the face of adversity. Ultimately, the journey toward understanding and tackling pattern baldness is a testament to the continuous advancements in science and the ongoing quest for individual well-being.
Conclusion
Pattern baldness is more common in men primarily due to genetic factors and hormonal influences, particularly the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This androgen causes hair follicles to shrink, leading to thinner hair and eventually hair loss. While women can also experience pattern baldness, the process tends to be less pronounced due to lower levels of DHT. Understanding the underlying causes of male pattern baldness is crucial in seeking effective treatments and preventive measures, allowing men to better manage and address hair loss concerns.
LATEST POSTS








