Sleeping After a Hair Transplant
Undergoing a hair transplant can be a transformative experience, offering individuals a renewed sense of self and confidence. However, it comes with its own set of challenges, especially in the critical days immediately following the procedure. Among these challenges, sleeping comfortably after a hair transplant is often at the forefront of patients' minds. This article seeks to address the intricacies surrounding sleep post-transplant, providing practical insights and strategies to enhance rest during this crucial recovery phase.
1. Understanding Post-Hair Transplant Discomfort
It's important to acknowledge that the initial phase following a hair transplant is not purely about excitement for the new hair growth; it can also involve discomfort and adjustments that might disrupt your usual sleep patterns. Understanding the various factors contributing to this discomfort can prepare you for a more restful recovery.
1.1. Swelling and Its Effects
Swelling is a common phenomenon after a hair transplant. This occurs as part of the body’s healing response and can lead to feelings of tightness across the scalp. The swelling usually peaks within the first couple of days but can vary depending on individual healing rates.
The presence of swelling can significantly affect how you feel during rest. When the scalp swells, it can put pressure on the newly grafted follicles, leading to a heightened sense of sensitivity. Additionally, an increase in swelling may make it uncomfortable to find a suitable sleeping position, resulting in restless nights.
To mitigate the effects of swelling, elevating your head while sleeping is highly recommended. By using extra pillows or a wedge pillow, you can help ensure that any excess fluid drains away from the scalp, reducing the intensity of the swelling overnight.
1.2. Scabbing and Itching
In addition to swelling, tiny scabs typically form over the newly grafted areas as they begin to heal. While these scabs are a natural part of the healing process, they can cause itchiness and tenderness. Itchiness can be particularly bothersome when trying to settle down for the night, potentially leading to the temptation to scratch-something that should be avoided at all costs. Scratching can dislodge grafts and introduce bacteria into healing wounds, which could compromise the success of the transplant.
To cope with the discomfort, consider applying ice packs wrapped in a cloth to the affected areas. This will not only provide relief from itching but also help manage inflammation. Additionally, antihistamines can help diminish itchiness, making it easier to focus on getting some well-deserved sleep.
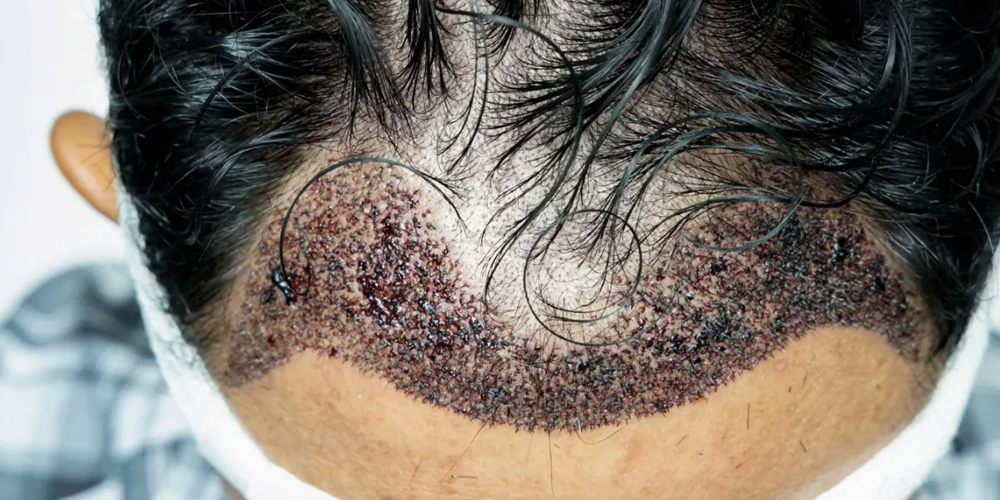
1.3. Pain Management
Though hair transplants are generally performed under local anesthesia, it is not uncommon for patients to experience mild pain or discomfort in both the donor and recipient areas afterward. The level of discomfort varies among individuals, depending on their pain threshold and the extent of the surgery.
Managing pain effectively plays a significant role in your ability to achieve restful sleep. Your doctor will likely prescribe medication to help alleviate pain in the initial days following the procedure. It is essential to take these medications as directed to ensure optimal comfort at night, enabling you to relax and drift off without constant interruptions.
2. The Importance of Sleep
As a cornerstone of the body's healing process, adequate sleep cannot be overstated, especially following a surgical procedure like a hair transplant. Quality rest contributes significantly to multiple aspects of recovery, helping to ensure that the grafts take hold successfully.
2.1. Repairing Tissues
Sleep is fundamental for tissue repair and regeneration. During deep sleep stages, the body releases growth hormones, which play a critical role in repairing damaged tissues. For someone recovering from a hair transplant, this means that those precious hours spent asleep are actively working to encourage healthy hair growth and minimize scarring.
Furthermore, quality sleep aids in the production of proteins necessary for cell communication and overall health. If you aren’t able to achieve restorative sleep, the healing process may be delayed, potentially impacting the results of your transplant.
2.2. Reducing Inflammation
A lack of sleep can exacerbate inflammation, a natural response the body has as it works to heal itself. When you sleep poorly, inflammatory markers can rise, which may prolong swelling and discomfort in the scalp after a hair transplant. This cycle can become counterproductive, creating a scenario where you’re unable to rest properly because of increased discomfort, which in turn prolongs healing.
Prioritizing quality sleep can help break this cycle. The anti-inflammatory responses triggered by proper rest assist in reducing overall inflammation, promoting quicker recovery times and lessening the severity of symptoms like swelling and pain.
2.3. Improving Immune Function
Another important aspect of sleep is its impact on immune function. A well-rested body boasts a stronger immune system, which plays a vital role in warding off infection during recovery. Following a hair transplant, the skin is healing, and any introduction of pathogens could lead to complications affecting the outcome of your transplant.
By ensuring that you get adequate sleep, you bolster your immune defenses. This protective layer assists in minimizing risks associated with infections, which can be detrimental to both your immediate recovery and long-term hair growth results.
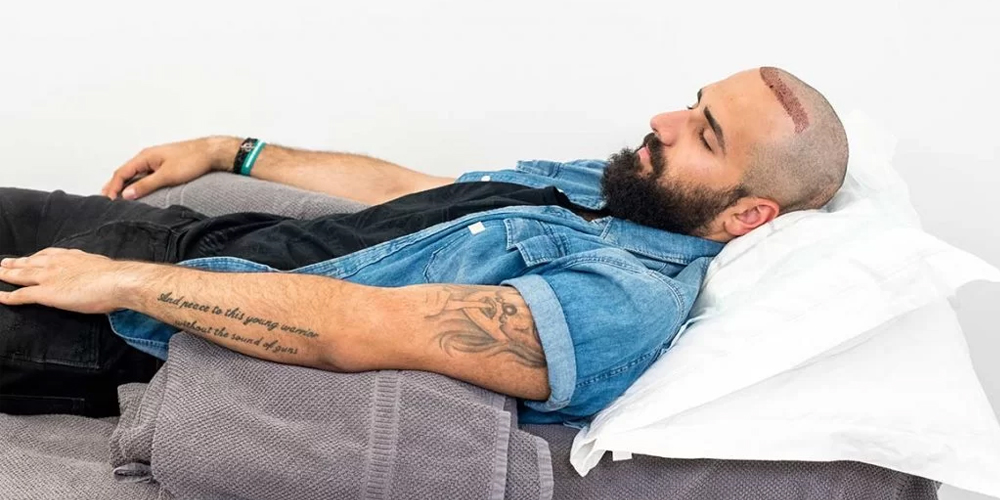

3. Sleep Strategies for Post-Transplant Recovery
Navigating the nuances of sleep following a hair transplant involves implementing several strategies designed to facilitate restful nights. As you adjust to your new reality, consider the following approaches to create a conducive sleeping environment.
3.1. The First Night: Preparing for Rest
Your first night after the procedure is crucial. It sets the tone for your overall recovery and can influence how easily you transition into a restful state. There are specific steps you can take to maximize your comfort.
Elevate Your Head: Keeping your head elevated during sleep is vital for managing swelling. By employing multiple pillows to prop yourself up, you'll reduce the likelihood of fluid accumulation around the scalp. This simple adjustment promotes proper drainage, resulting in a lesser degree of discomfort as you try to settle in for the night.
Avoid Direct Pressure: It is equally important to avoid putting direct pressure on the grafted area. This means sleeping on your back is preferable, as engaging in side sleeping or stomach sleeping poses a greater risk of dislodging the grafts. Taking care to maintain a position that avoids pressure will help ensure your hard-earned follicles remain intact.
Opt for a Soft Pillow: Using a soft and comfortable pillow enhances your chances of falling asleep quickly. Some people find relief in specially designed pillows for side sleepers, which help align the neck and head, distributing weight more evenly across the surface. Choosing the right pillow can make a considerable difference in how well you sleep during this sensitive time.
3.2. Beyond the First Night: Continuing Care
Once the initial days have passed, it remains essential to continue employing effective sleep strategies that support ongoing comfort and healing.
Maintain a Cool and Comfortable Environment: Creating a relaxing sleep environment goes a long way towards achieving quality rest. Keeping your bedroom cool and well-ventilated can help regulate your body temperature during sleep, preventing overheating and discomfort. You may also benefit from blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines to eliminate distractions and foster a tranquil ambiance.
Follow Pain Medication Guidelines: Adhering to your doctor's prescribed pain management plan is critical. These medications can aid in both comfort and relaxation, easing you into a peaceful slumber. If you find certain medications are interfering with your ability to stay awake during the day or feel groggy, consult your healthcare provider for alternative options.
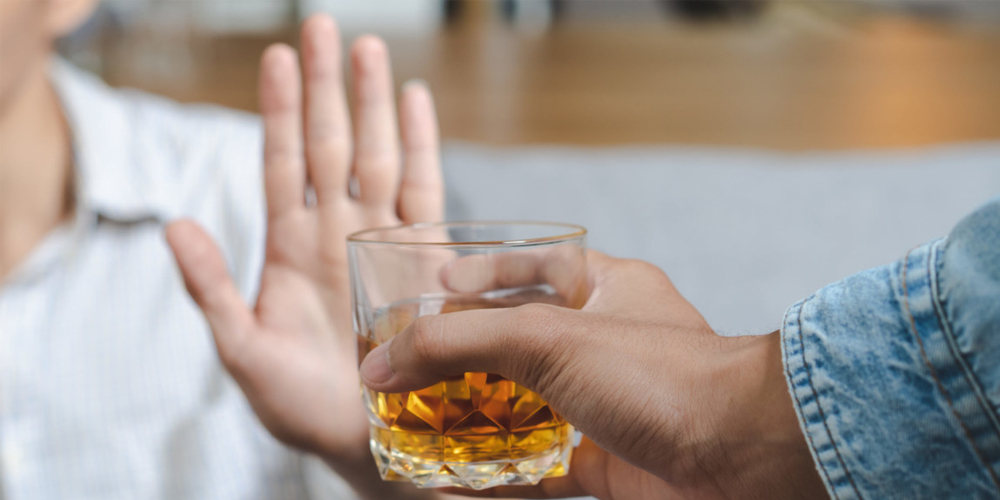
Limit Alcohol and Caffeine Intake: Both alcohol and caffeine can negatively impact sleep quality. Alcohol may initially help you fall asleep but disrupts sleep cycles, leading to a less restorative slumber. Caffeine, on the other hand, is a stimulant that can keep you alert longer than desired. Avoiding these substances, particularly in the days following your hair transplant, will promote a smoother recovery and better sleep overall.

3.3. Creating a Soothing Bedtime Routine
Establishing a calming bedtime routine can greatly improve your ability to unwind before sleep. Engaging in relaxing activities signals to your body that it's time to wind down, allowing you to prepare mentally and physically for rest.
Engage in Relaxing Activities: Take time each evening to indulge in activities that promote relaxation. This could include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing meditation. Engaging in such practices can help lower cortisol levels, reducing stress and preparing your body for a good night's rest.
Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule: Consistency is key when it comes to sleep. Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your circadian rhythms, making it easier to fall asleep initially and enjoy uninterrupted rest.
3.4. Addressing Common Sleep Concerns
Despite your best efforts, you may still encounter specific concerns related to sleep during your recovery. Being prepared and informed about potential issues can help you navigate them more successfully.
Itchiness and Irritation: Itchiness is common after a hair transplant, and the incessant urge to scratch can become overwhelming. Resisting the temptation to scratch is essential, as it can lead to complications. Instead, use gentle methods to soothe the area; this may include applying a cool compress to relieve irritation and taking antihistamines as needed.
Managing Swelling Effectively: As previously noted, swelling is an expected part of recovery. To promote a speedy reduction in swelling, elevate the head while sleeping and apply cool compresses to the area. If swelling becomes excessive or is accompanied by severe discomfort, contact your physician promptly for further guidance.
Dealing with Discomfort: Experiencing discomfort is normal after a hair transplant. If you find the pain is significantly hindering your ability to sleep, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor. They may suggest alternative medication options or techniques to ensure you are as comfortable as possible.
Conclusion
Sleeping after a hair transplant may require some adjustments, but understanding the significance of rest and employing strategic techniques will help enhance your recovery experience. By focusing on proper sleep hygiene, utilizing supportive equipment, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, you can navigate this challenging phase with greater ease.
Ultimately, patience is key as you embrace your journey toward fuller hair and improved self-confidence. With dedication to your recovery and attention to your physical and mental well-being, restful nights will pave the way for successful healing, ensuring that you emerge from this experience feeling revitalized and ready to face the world with renewed vigor.
LATEST POSTS








