Male Pattern Baldness: How to Treat and Prevent Hair Loss
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a condition that affects millions of men around the globe. It typically manifests as a gradual thinning of hair on the scalp, often starting at the temples or crown and progressing over time. While not life-threatening, male pattern baldness can have profound effects on self-esteem and confidence. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of male pattern baldness, including its causes, treatment options, and preventive measures to help manage this common condition effectively.
1. Understanding the Roots of Male Pattern Baldness
1.1. The Role of Genetics and Hormones
The primary drivers of male pattern baldness are genetics and hormones. If you have a family history of baldness, your chances of experiencing hair loss increase significantly. Genetic predisposition means that certain genes inherited from both parents can make hair follicles more susceptible to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone.
DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, leading to a process called miniaturization. During miniaturization, hair follicles shrink over time, producing thinner and weaker hair strands. Eventually, these follicles may stop producing hair altogether, resulting in permanent hair loss. Understanding this hormonal influence is crucial for anyone seeking to address their hair loss concerns.
1.2. Age-Related Changes
As men age, their bodies undergo various hormonal changes, including a decrease in testosterone production. Interestingly, while testosterone levels drop, the sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT often increases. This heightened sensitivity means that even lower levels of testosterone can still trigger the miniaturization process, leading to hair loss.
Age-related changes can complicate the situation further, as older men may experience a combination of genetic predisposition and increased follicle sensitivity. This dual impact can accelerate the progression of male pattern baldness, making it essential to adopt proactive measures early on.

1.3. Other Factors
While genetics and hormones are the primary culprits behind male pattern baldness, several other factors can contribute to hair loss. Stress is one such factor; chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels and blood flow to the scalp, potentially exacerbating hair loss.
Smoking is another contributor, as the toxins found in cigarettes can harm hair follicles and hinder growth. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or iron deficiency anemia, can lead to hair loss. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly a lack of essential vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and biotin, can also negatively affect hair health. Lastly, some medications, including chemotherapy drugs and blood thinners, may cause temporary hair loss as a side effect.
2. Recognizing the Signs of Male Pattern Baldness
2.1. Receding Hairline
One of the earliest signs of male pattern baldness is a receding hairline. Typically, this occurs in an M-shaped pattern, where the hairline gradually moves back from the forehead. This change can be subtle at first, but over time, it becomes more pronounced, often leading to a U-shaped hairline as the balding progresses.
Recognizing this initial sign is crucial for early intervention. Many men may dismiss minor changes in their hairline, but being aware of these shifts can prompt them to seek professional advice sooner rather than later.
2.2. Thinning Crown
Another common indicator of male pattern baldness is thinning hair on the crown of the head. This area may develop a bald spot that gradually expands over time. As the hair in this region becomes finer and sparser, it can create a noticeable contrast with the surrounding hair, making the thinning more apparent.
Monitoring changes in the crown area can help individuals gauge the progression of their hair loss. If you notice increased thinning or a developing bald spot, consulting a dermatologist or trichologist can provide valuable insights into potential treatment options.
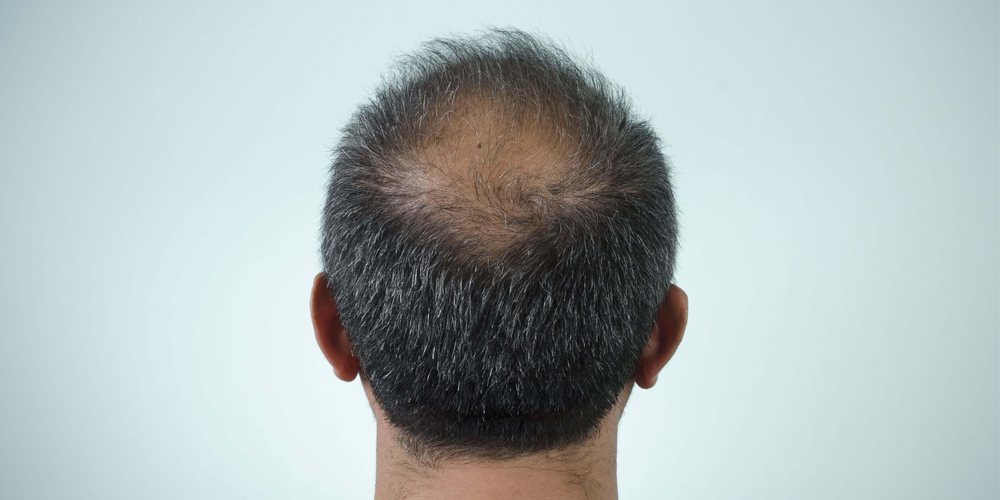
2.3. Overall Hair Thinning
In addition to localized changes, male pattern baldness often leads to overall hair thinning across the scalp. Hair may become finer and less dense, resulting in larger gaps between strands. This thinning can be distressing for many men, as it alters their appearance and can diminish self-confidence.
Understanding the broader implications of hair thinning is essential for managing expectations regarding treatment outcomes. While some treatments may promote regrowth in specific areas, they may not fully restore overall hair density.
2.4. Hair Loss
Ultimately, as male pattern baldness progresses, hair follicles may shrink to the point where they cease producing new hair altogether. This stage results in permanent hair loss, which can be emotionally challenging for many men.
If you notice any of these signs, it's essential to consult a dermatologist or trichologist for proper diagnosis and guidance. They can rule out other potential causes of hair loss and recommend the most effective treatment options tailored to your unique situation.
3. Treatment Options for Male Pattern Baldness
3.1. Medications
Medications represent one of the most common approaches to managing male pattern baldness. Two widely recognized options are Minoxidil and Finasteride.
Minoxidil, available over the counter under brand names like Rogaine, is a topical solution that stimulates hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp. Users typically apply it directly to the affected areas, and consistent use over several months is necessary to see results. While Minoxidil can slow down hair loss and promote regrowth in some cases, it requires ongoing application to maintain its effects.
Finasteride, on the other hand, is an oral prescription medication that works by blocking the enzyme responsible for converting testosterone to DHT. By reducing DHT levels, Finasteride can slow down or even halt hair loss for many men. However, results may vary, and sustained use is essential to achieve and maintain benefits. Some users may experience side effects, so discussing these risks with a healthcare provider is crucial before starting treatment.
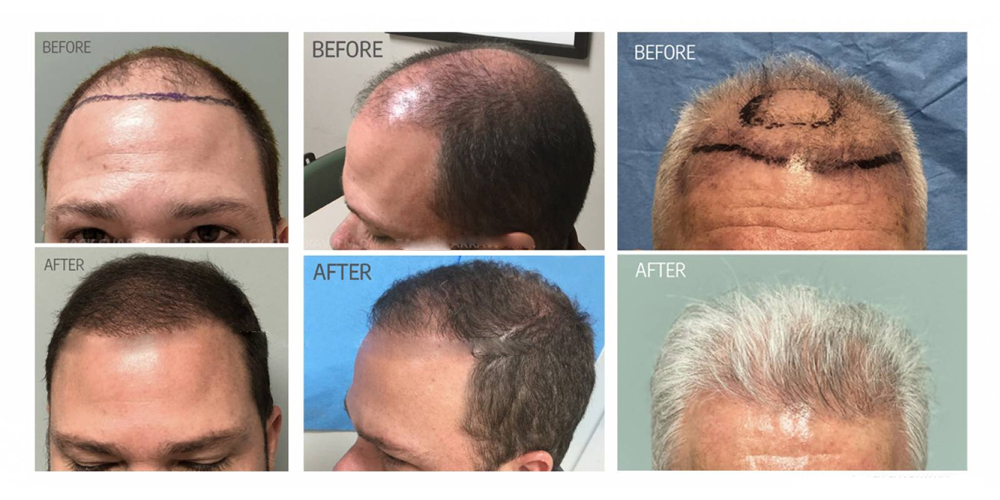
3.2. Hair Transplants
For those seeking a more permanent solution, hair transplantation offers a surgical option. This procedure involves removing hair follicles from a donor area, typically located at the back of the head, and transplanting them to the balding regions.
Hair transplants can yield natural-looking results and provide a long-lasting solution to hair loss. However, the procedure can be relatively expensive and may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired outcome. It's essential to research qualified professionals and clinics to ensure a successful procedure.
3.3. Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is another non-invasive treatment option gaining popularity among men experiencing hair loss. This technique uses red light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
LLLT is considered safe and painless, making it an attractive alternative for those hesitant about surgical procedures. Many individuals choose to combine laser therapy with other treatments for optimal results. While research is still ongoing, preliminary studies suggest that LLLT may enhance hair density and improve overall scalp health.
3.4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets derived from the patient's blood into the scalp. These platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate hair growth and improve the overall health of hair follicles.
PRP therapy is minimally invasive and has shown promising results in some cases. Patients typically undergo a series of sessions to maximize benefits. However, individual responses to PRP therapy can vary, and it's essential to consult with a qualified practitioner to determine if this treatment is appropriate for your situation.
3.5. Scalp Micropigmentation
For those looking for a cosmetic solution to conceal bald spots, scalp micropigmentation offers an innovative approach. This procedure involves tattooing tiny dots of pigment onto the scalp to mimic the appearance of hair follicles.
Scalp micropigmentation can create the illusion of a fuller head of hair and is a relatively less expensive option compared to hair transplants. However, it's important to note that this is not a permanent solution and requires regular touch-ups to maintain the desired look.
4. Preventing Further Hair Loss
4.1. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet plays a vital role in maintaining healthy hair. Consuming foods rich in protein, iron, zinc, biotin, and omega-3 fatty acids can support hair growth and help prevent shedding. Incorporating lean meats, fish, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables into your meals can provide essential nutrients for optimal hair health.
On the other hand, minimizing processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol consumption is equally important. These substances can hinder nutrient absorption and negatively impact overall health, including hair quality. Prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods can create a solid foundation for hair health.
4.2. Stress Management
Managing stress is crucial for overall well-being, and it can also play a significant role in preventing hair loss. Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels and blood flow to the scalp, potentially exacerbating hair loss.
Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and spending time in nature can help alleviate stress levels. Additionally, prioritizing adequate sleep allows the body to repair and regenerate, contributing to healthy hair growth. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a calming bedtime environment can enhance sleep quality.
4.3. Healthy Scalp Practices
Maintaining a healthy scalp is essential for promoting hair growth and preventing further hair loss. Using gentle shampoos and conditioners free from harsh chemicals and sulfates can help preserve the scalp's natural oils. These products can minimize dryness and irritation, creating a healthier environment for hair follicles.
Avoiding tight hairstyles and excessive heat styling is also crucial, as these practices can damage hair follicles and contribute to hair loss. Regularly massaging the scalp can improve blood flow and promote hair growth. Consider incorporating scalp massages into your routine to enhance circulation and nourish hair follicles.
Conclusion
Male pattern baldness is a common condition that affects countless men worldwide. While it may seem daunting, understanding the roots of hair loss, exploring treatment options, and adopting preventative measures can empower you to manage this condition effectively. Remember that your overall well-being goes beyond your hair, and embracing self-acceptance is vital in maintaining a positive self-image despite hair loss. With the right knowledge and support, you can navigate your hair loss journey with confidence and resilience.
LATEST POSTS








