Hair transplant: How does it work?
The concept of a hair transplant has gained immense popularity in recent years as individuals seek effective solutions for hair loss. A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves relocating hair follicles from one part of the body, typically the back or sides of the scalp, to areas experiencing thinning or balding. This innovative approach not only restores hair growth but also enhances self-esteem and confidence, giving patients a new lease on life. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricate workings of hair transplants, exploring the various techniques, potential benefits, and crucial considerations involved.
1. Understanding Hair Loss
Before diving into the mechanics of hair transplant procedures, it’s essential to understand the underlying causes of hair loss. Recognizing these factors can provide insight into why a hair transplant might be necessary and how it can effectively restore one's appearance.
1.1. The Biological Basis of Hair Growth
Hair growth is a complex biological process that occurs in cycles. Each hair follicle goes through a growth phase (anagen), a resting phase (telogen), and eventually falls out.
The hair growth cycle is influenced by numerous factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental conditions.
When hair follicles stop producing hair, whether due to genetic predisposition, such as androgenetic alopecia, or other factors like stress or nutritional deficiencies, thinning or baldness can occur. Understanding this cycle helps in comprehending why some individuals may require a hair transplant to regain their lost hair.
1.2. Types of Hair Loss
Several types of hair loss are prevalent among individuals today.
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, is characterized by gradual thinning and is often hereditary.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition resulting in patchy bald spots, while telogen effluvium is caused by physical or emotional stress leading to temporary hair loss.
Each type has its unique characteristics and implications for treatment, with hair transplants primarily targeting those suffering from pattern baldness.
1.3. Psychological Impact of Hair Loss
The effects of hair loss extend beyond physical appearance and can lead to significant psychological distress.
Many individuals experience feelings of embarrassment, low self-esteem, or chronic anxiety regarding their appearance.
This emotional toll often drives people to seek out solutions, making a hair transplant not just a cosmetic procedure but a life-changing intervention that can improve overall quality of life.

2. Hair Transplant Techniques
There are various methods employed in hair transplantation, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these techniques is vital for anyone considering a hair transplant.
2.1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also known as strip harvesting, involves removing a strip of skin containing hair follicles from the donor site.
The harvested area is then sutured, leaving a linear scar that can be concealed by surrounding hair.
After obtaining the strip, the surgeon dissects it into individual follicular units containing one to four hairs.
These units are then meticulously transplanted into the balding areas of the scalp.
The FUT technique is particularly advantageous for individuals requiring extensive coverage as it allows for a larger number of grafts to be harvested at once. However, the linear scar can be a concern for those opting for shorter hairstyles.
2.2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is another popular method, which differs significantly from FUT.
In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the scalp using a specialized tool without the need for a surgical incision.
This minimally invasive approach results in tiny, dot-like scars that are less noticeable compared to the linear scar associated with FUT.
FUE is favored for its quicker recovery time and less postoperative discomfort. Additionally, many candidates prefer FUE due to its ability to leave minimal scarring, making it suitable even for those who desire very short haircuts.
2.3. Robotic-Assisted Hair Transplantation
With advancements in technology, robotic-assisted hair transplantation has emerged as a cutting-edge option within the field of hair restoration.
Using sophisticated algorithms and precision tools, robotic systems can assist surgeons in identifying and extracting hair follicles more accurately than traditional methods.
Robotic-assisted systems increase the efficiency of both FUE and FUT techniques, resulting in enhanced graft survival rates and reduced trauma to the scalp.
However, it's important to note that while robotics play a role in the extraction process, skilled human intervention remains critical for successful placement and overall outcome.
2.4. Choosing the Right Technique
The selection of a specific hair transplant technique depends on various factors, including the individual's level of hair loss, desired outcome, and personal preferences.
Consulting with a qualified hair restoration specialist is crucial, as they can assess your unique situation and guide you toward the most appropriate method.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each technique can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their hair restoration journey.
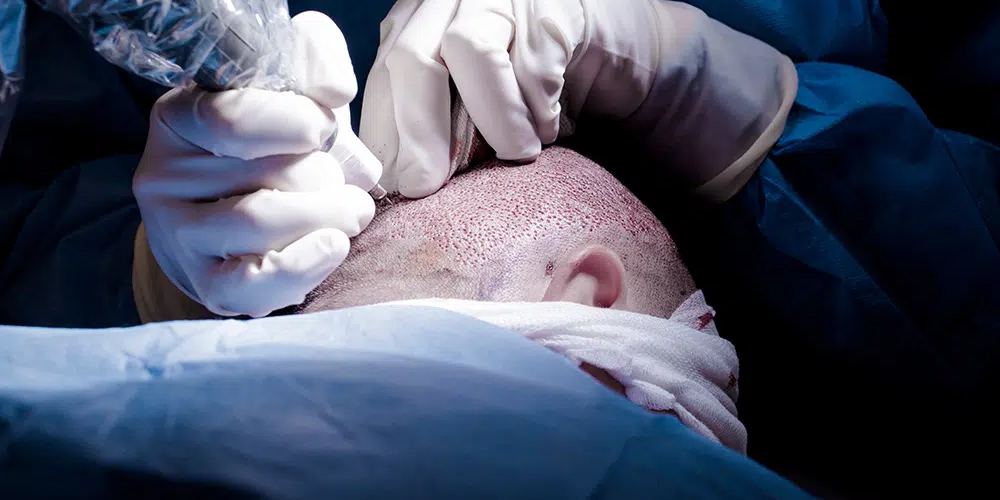
3. The Surgical Process
Understanding the surgical process involved in a hair transplant is key to alleviating any concerns one might have before undergoing the procedure.
3.1. Pre-Operative Considerations
Prior to the surgery, a thorough consultation is conducted to evaluate the patient's medical history, extent of hair loss, and suitability for the procedure.
During this phase, patients are encouraged to discuss their expectations and ask questions.
Additionally, patients may be advised to avoid certain medications, such as blood thinners, and refrain from alcohol consumption in the days leading up to the surgery to minimize potential complications.
3.2. The Day of the Procedure
On the day of the surgery, patients typically arrive at the clinic early in the morning.
Local anesthesia is administered to ensure that the patient remains comfortable throughout the procedure.
The surgeon then begins the process, either by harvesting a strip of skin (for FUT) or using a punch tool to extract individual follicles (for FUE).
Depending on the extent of the hair transplant, the duration of the procedure can range from several hours to an entire day.
3.3. Post-Operative Care
Following the surgery, patients receive detailed instructions regarding post-operative care to promote healing and maximize graft survival.
It is common to experience mild discomfort, swelling, or redness in the treated area, which typically resolves within a few days.
Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, direct sunlight, and excessive manipulation of the scalp during the initial healing phase.
Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor progress and address any concerns.
Understanding the full spectrum of the surgical process can help reassure prospective patients about what to expect and enable them to prepare adequately for their hair transplant journey.
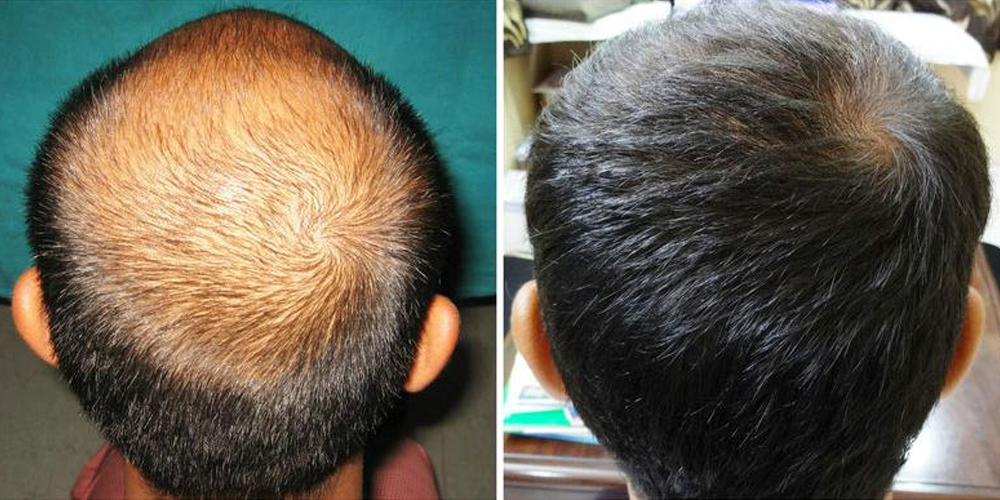
4. Recovery and Results
Recovery following a hair transplant is a critical phase in determining the success of the procedure.
4.1. Immediate Recovery
In the days immediately following the transplant, patients may notice scabs forming around the newly implanted hair follicles.
This is a normal part of the healing process, and patients must be careful not to scratch or pick at these scabs, as doing so could dislodge the grafts.
Mild pain or discomfort can typically be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, though prescription medications may be provided if necessary.
During this period, it is essential to adhere to all post-operative care guidelines, which may include gentle washing of the hair, avoiding hair products, and wearing protective headgear when going outdoors.
4.2. Long-Term Healing
As the weeks progress, the transplanted hair will initially shed-a phenomenon known as "shock loss."
This shedding is a normal occurrence and should not cause alarm, as the hair follicles enter a resting phase before entering the anagen phase again.
About three to six months following the procedure, patients will begin to notice new hair growth.
The rate of growth varies per individual, but typically, a fuller result can be expected between six months to one year after the surgery.
4.3. Managing Expectations
While hair transplants offer remarkable improvements, managing expectations is crucial.
Factors such as individual response to the procedure, hair density, and the skill of the surgeon all play roles in the final outcome.
Realistic expectations can prevent disappointment and help individuals appreciate the transformative effect of their hair transplant.
Moreover, maintaining open communication with the surgeon throughout the healing process ensures that any concerns can be addressed promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a hair transplant offers an innovative solution for individuals grappling with hair loss. By understanding the underlying causes of hair loss, the various techniques available, the surgical process, and the recovery timeline, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their hair restoration journey.
LATEST POSTS








